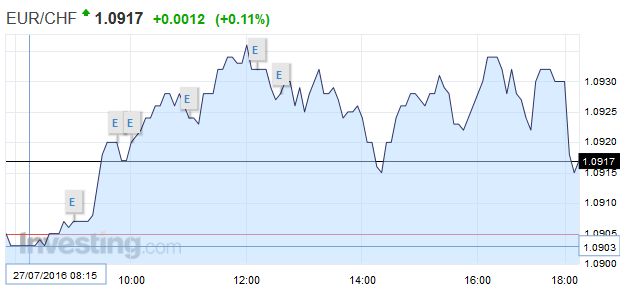
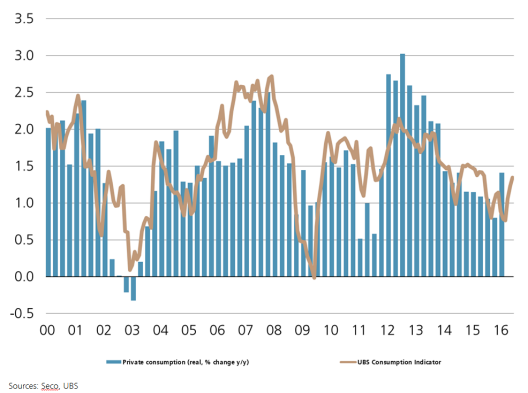
Swiss Franc The Euro kept on climbing, after yesterday’s rapid rise. Click to enlarge. The Swiss consumption indicator by UBS shows improvements. The indicator is still distant from the highs in 2012. At the time stronger growth in Emerging Markets and the weaker franc helped the Swiss economy. Switzerland UBS Consumption Indicator Japan As uncertainty over Japan’s fiscal stimulus roiled the yen and domestic equities, Prime Minister Abe was forced to announce his fiscal intentions earlier than he initially intended. The JPY27 trillion (~5 bln) package. The details are far from clear, which may help explain why the dollar is in the middle of the two yen range (~JPY104.65-JPY106.55). Note the high for the week was set on Monday near JPY106.70. An unspecified part of the spending will be included in fall supplemental budget, which Japan regularly introduces. In addition, there is no distinction between spending and programs that offer low interest rate loans. It is also not clear how much new borrowing in entailed or how it will be done. A Dow Jones report claiming the introduction of 50-year government bonds was denied.
Topics:
Marc Chandler considers the following as important: AUD, EUR, Eurozone M3 Money Supply, Featured, FX Daily, FX Trends, GBP, JPY, newsletter, U.K. Gross Domestic Product, U.S. Core Durable Goods Orders, U.S. Pending Home Sales, USD
This could be interesting, too:
Eamonn Sheridan writes CHF traders note – Two Swiss National Bank speakers due Thursday, November 21
Charles Hugh Smith writes How Do We Fix the Collapse of Quality?
Marc Chandler writes Sterling and Gilts Pressed Lower by Firmer CPI
Michael Lebowitz writes Trump Tariffs Are Inflationary Claim The Experts
Swiss FrancThe Euro kept on climbing, after yesterday’s rapid rise. |
|
| The Swiss consumption indicator by UBS shows improvements. The indicator is still distant from the highs in 2012. At the time stronger growth in Emerging Markets and the weaker franc helped the Swiss economy. |
Japan
As uncertainty over Japan’s fiscal stimulus roiled the yen and domestic equities, Prime Minister Abe was forced to announce his fiscal intentions earlier than he initially intended. The JPY27 trillion (~$265 bln) package.
The details are far from clear, which may help explain why the dollar is in the middle of the two yen range (~JPY104.65-JPY106.55). Note the high for the week was set on Monday near JPY106.70. An unspecified part of the spending will be included in fall supplemental budget, which Japan regularly introduces.
In addition, there is no distinction between spending and programs that offer low interest rate loans. It is also not clear how much new borrowing in entailed or how it will be done. A Dow Jones report claiming the introduction of 50-year government bonds was denied.
Another reason that Abe may have felt compelled to announce the size of the fiscal plan, which we suggest is flattered by combining programs and the like, is to create a set of optics that would encourage not only immediate support for the stock market (Nikkei rallied 1.7%) but also to encourage the BOJ to be similarly bold.
There had been conflicting media reports about the fiscal stimulus, and there has been no better clarity into the BOJ’s action at the end of the week. A newswire poll found 80% of the surveyed expect the BOJ to take some action, with an increase in ETF purchases most favored. However, this alone would not likely satisfy the government or investors. There is talk of adding to it JGB purchases, for which the new supply is not yet publicly known.
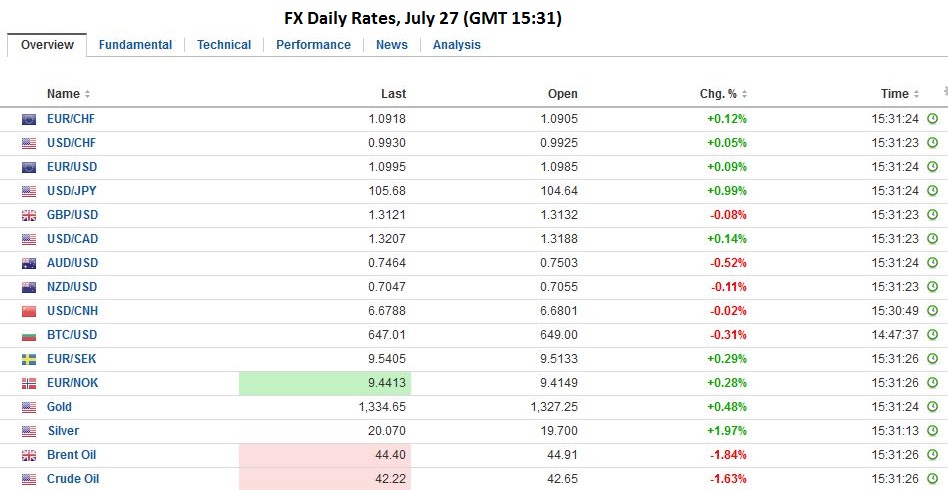
FX RatesThis week sterling has been capped in the $1.3165-$1.3175 area. The lower end of the range seems to be around $1.3060. Similarly, the euro has been carving out a shelf in the GBP0.8340-GBP0.8350 area, above last week test on GBP0.8300 and the previous week GBP0.8250. At the same time, despite the probes, it has not been able to establish a foothold back above GBP0.8400. The Australian dollar also has been whipsawed by uncertainty over the policy outlook. The market went into the Q2 CPI report leaning (~almost 60% chance according to the derivatives market) toward a rate cut next week. The headline CPI rose 0.4% in Q2 for a 1.0% year-over-year rate, down from 1.3% in Q1. This is the slowest pace in almost 20 years. The RBA puts more emphasis on the trimmed mean and weighted median measures. The former was a little firmer than expected, unchanged at 1.7%, while at 1.3% the latter was as expected. The market reduced the perceived chances of a rate cut next week to nearly a 50-50 proposition. The Australian dollar initially rallied to around half a cent to $0.7565 but then dropped like a stone and briefly slipped through yesterday’s lows. It has been chopping around a $0.7475-$0.7495 range through the European morning. On balance, we are still are inclined to look for a rate cut next week. |
|
United KingdomNews that the UK grew faster than expected in Q2 was unable to sustain the higher sterling bias seen in Asia. The UK’s first estimate for Q2 GDP draws on around half the data. It was 0.6% after a 0.4% pace in Q1. The year-over-year rate ticked up to 2.2%. The 2.1% surge in industrial production was front loaded in the quarter, but its was the largest increase since the late 1990s. Manufacturing and energy output were strong. Services rose 0.5%, while construction fell 0.4%. |
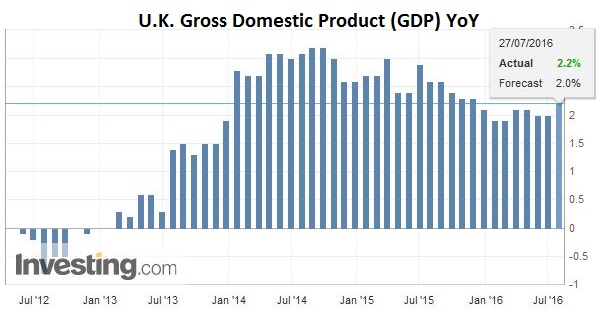 Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com |
EurozoneEurozone money supply and lending figures were reported. As expected M3 rose 5.0% year-over-year. Lending to non-financial corporation and households edged higher to 1.7%. The news was unable to breathe fresh life into the lethargic euro trading. The single currency was confined to less than a quarter cent range. It has yet to make a convincing break of the $1.10 level but is spending more time below it than above it. |
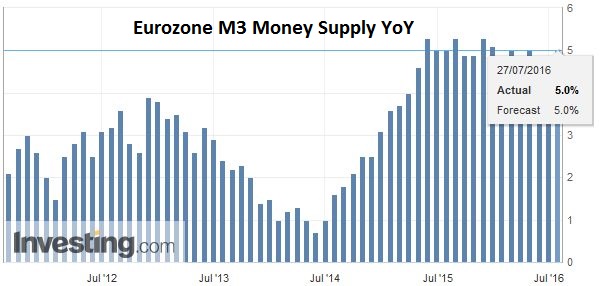 Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com |
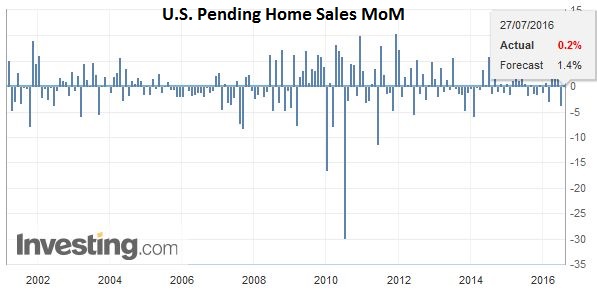
United StatesThe US reports durable goods orders and pending home sales prior to the release of the FOMC statement, which is the highlight of the session. The details of the durable goods orders report will likely be better than the headline. The report could also impact last minute adjustments to Q2 GDP estimates. Pending home sales are expected to recoup some of the weakness seen in May. |
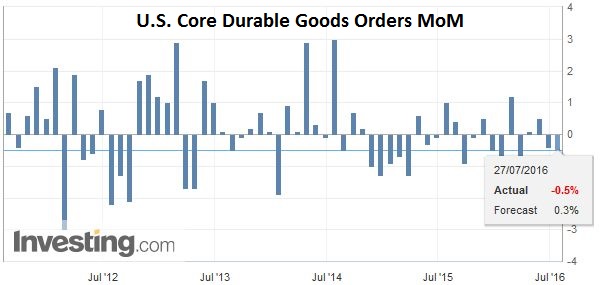 Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com |
| We expect the FOMC statement to reflect the greater confidence than was apparent in June. Economic data has been firm. Activity seemed to pick-up in June. The global markets have been fairly resilient in the face of the Brexit decision, the coup in Turkey (and the bloody aftermath), as well as the depreciation of the Chinese yuan and Chinese stocks. The re-introduction of the risk-assessment would be a way that the Fed can signal that it is still prepared to raise interest rates. This could point can also be underscored if there another official joins George in dissenting from the steady policy the majority will back. |
 Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com |
China
Speaking of Chinese stocks, a large loss was recorded Shenzhen (-4.5%) and somewhat smaller loss in Shanghai (-2.0%), even though the MSCI Asia-Pacific Index managed to rise 0.25% and extend its gains for a third session. Reports have linked the sell-off reports that the regulators are going to curb the wealth management products from investing in some equities and other assets, such as loans.
Graphs and additional information on Swiss Franc by the snbchf team.