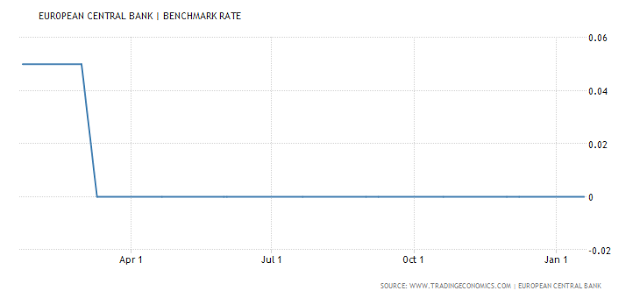
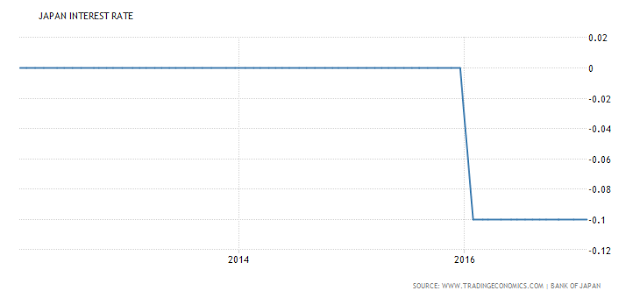
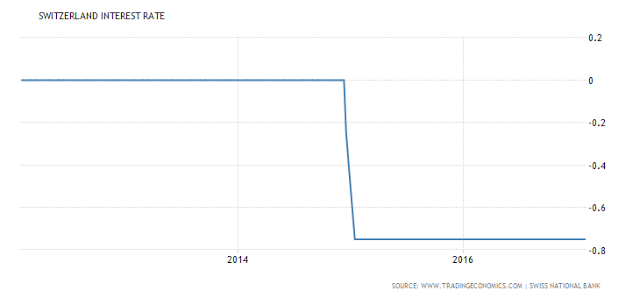
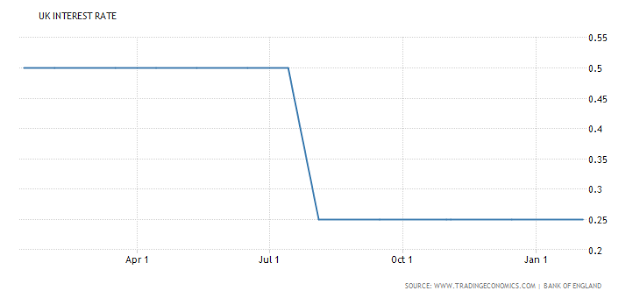
We discuss the rate differentials between Switzerland, Britain, Europe, Japan and the United States and how this Developed Financial Markets carry trade is incentivizing excessive risk taking with tremendous leverage and destabilizing the entire financial system in the process in this video. You want to know what is behind weekly market records, borrowed money via punchbowl central bank liquidity. This ends badly every time Central Banks. You can run this model 1 Million iterations, and it plays out the same way, the financial bubble implodes in on itself where liquidity evaporates into nothingness. It is ironic that when the bubble pops, given all the Central Bank infused liquidity to create this bubble paradigm, that all liquidity dries up, and all the sudden there is no real liquidity at all in the system when everyone direly needs it! European Central Bank European Central Bank Interest Rates - March 2016 - 2017 - Click to enlarge Japan Japan Interest Rates - 2013 - 2017 March - Click to enlarge Switzerland Switzerland Interest Rates - 2013 - 2017 March - Click to enlarge United Kingdom UK Interest Rates - March 2016 - 2017 - Click to enlarge United States US Interest Rates - March 2016 - 2017 - Click to enlarge Conclusion: Central Banks need a coordinated
Topics:
EconMatters considers the following as important: Bank, Banking, Business, Carry Trade, Central Banks, CHF, Economic bubble, economy, Featured, Federal Reserve, Finance, financial markets, Financial ratios, Financial risk, Interest Rate, Japan, Market liquidity, Monetary Policy, Money, newsletter, Risk Management, Switzerland, Systemic risk, Twitter, US Federal Reserve
This could be interesting, too:
Claudio Grass writes The Case Against Fordism
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Die Performance der Kryptowährungen in KW 9: Das hat sich bei Bitcoin, Ether & Co. getan
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Wer verbirgt sich hinter der Ethereum-Technologie?
Martin Hartmann writes Eine Analyse nach den Lehren von Milton Friedman
We discuss the rate differentials between Switzerland, Britain, Europe, Japan and the United States and how this Developed Financial Markets carry trade is incentivizing excessive risk taking with tremendous leverage and destabilizing the entire financial system in the process in this video. You want to know what is behind weekly market records, borrowed money via punchbowl central bank liquidity. This ends badly every time Central Banks. You can run this model 1 Million iterations, and it plays out the same way, the financial bubble implodes in on itself where liquidity evaporates into nothingness. It is ironic that when the bubble pops, given all the Central Bank infused liquidity to create this bubble paradigm, that all liquidity dries up, and all the sudden there is no real liquidity at all in the system when everyone direly needs it!
European Central Bank |
|
Japan |
Japan Interest Rates - 2013 - 2017 March |
Switzerland |
Switzerland Interest Rates - 2013 - 2017 March |
United Kingdom |
UK Interest Rates - March 2016 - 2017 |
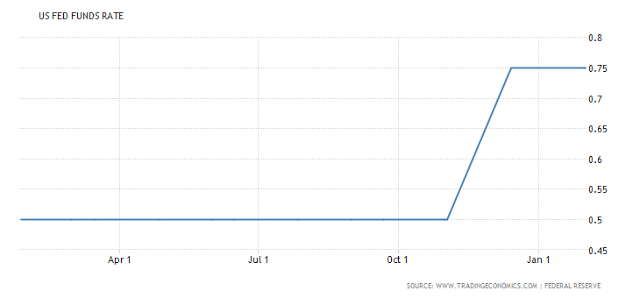
United States |
US Interest Rates - March 2016 - 2017 |
Conclusion:
Tags: Bank,Banking,Business,Carry Trade,central banks,Economic bubble,economy,Featured,Federal Reserve,Finance,Financial markets,Financial ratios,Financial risk,Interest Rate,Japan,Market liquidity,Monetary Policy,money,newsletter,Risk Management,Switzerland,Systemic risk,Twitter,US Federal Reserve