Finanz und Wirtschaft, December 9, 2020. PDF. Economic policy is not about GDP growth. It’s about welfare. Externalities are key. Infection externalities don’t go away by calling for responsible behavior. Infection externalities can turn positive. Keeping worthy companies or networks alive does not require government intervention, unless capital markets don’t work. To judge the right amount of burden sharing is beyond economics. But economics gives some clues: In an ideal world,...
Read More »Why Aren’t Bond Yields Flyin’ Upward? Bidin’ Bond Time Trumps Jay
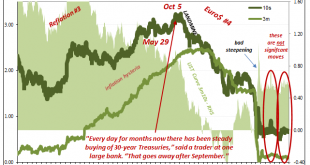
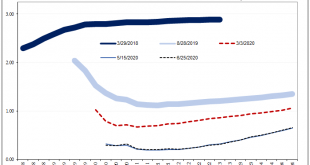
It’s always something. There’s forever some mystery factor standing in the way. On the topic of inflation, for years it was one “transitory” issue after another. The media, on behalf of the central bankers it holds up as a technocratic ideal, would report these at face value. The more obvious explanation, the argument with all the evidence, just couldn’t be true otherwise it’d collapse the technocracy right down to the ground. And so it was also in the bond market....
Read More »“Unabhängigkeit der Nationalbank (Independence of the SNB),” FuW, 2020
Finanz und Wirtschaft, July 25, 2020. PDF. The Swiss National Bank—yes, the Swiss one—feels it must remind politicians of its independence. Parliamentarians from left to right (!) voice demands. To shrink the SNB’s balance sheet? No, for more central bank profits to be distributed sooner rather than later. I discuss misconceptions, possible motivations, and a constructive response. «The best way to defend the independence of a central bank is never to exercise it.»
Read More »“Monetäre Staatsfinanzierung mit Folgen (Monetary Financing of Government),” Die Volkswirtschaft, 2020
Die Volkswirtschaft, 24 July 2020. PDF. Clarifying the connections between outright monetary financing, QE, the distribution of seignorage profits, the relationship between fiscal and monetary policy, and central bank independence. Abstract: Wenn Parlamentarier höhere Gewinnausschüttungen der Nationalbank fordern, Kritiker im Euroraum mehr «Quantitative Easing» oder Helikoptergeld verlangen und andere Stimmen monetäre Staatsfinanzierung monieren, dann steht die Beziehung zwischen...
Read More »Wait A Minute, What’s This Inversion?
Back in the middle of 2018, this kind of thing was at least straight forward and intuitive. If there was any confusion, it wasn’t related to the mechanics, rather most people just couldn’t handle the possibility this was real. Jay Powell said inflation, rate hikes, and accelerating growth. Absolutely hawkish across-the-board. And yet, all the way back in the middle of June 2018 the eurodollar curve started to say, hold on a minute. That’s the part which caused so...
Read More »From QE to Eternity: The Backdoor Yield Caps
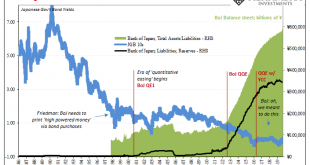
So, you’re convinced that low rates are powerful stimulus. You believe, like any good standing Economist, that reduced interest costs can only lead to more credit across-the-board. That with more credit will emerge more economic activity and, better, activity of the inflationary variety. A recovery, in other words. Ceteris paribus. What happens, however, if you also believe you’ve been responsible for bringing rates down all across the curve…and then no recovery....
Read More »“Wenn die Notenbank den Staat finanziert (When the Central Bank Finances the State),” FAS, 2020
FAS, 31 May 2020. PDF. Monetary deficit financing is the norm—after all, central banks distribute their profits. Monetary financing occurs in the context of regular open market operations and QE and, hyper charged, with helicopter drops. The question is not whether monetary policy should finance the government, but why it does so, and to what extent. Fiscal and monetary policy are inherently connected; what constitutes monetary policy is defined by objectives....
Read More »“Wenn die Notenbank den Staat finanziert (When the Central Bank Finances the State),” FAS, 2020
FAS, 31 May 2020. PDF. Monetary deficit financing is the norm—after all, central banks distribute their profits. Monetary financing occurs in the context of regular open market operations and QE and, hyper charged, with helicopter drops. The question is not whether monetary policy should finance the government, but why it does so, and to what extent. Fiscal and monetary policy are inherently connected; what constitutes monetary policy is defined by objectives.
Read More »A Big One For The Big “D”
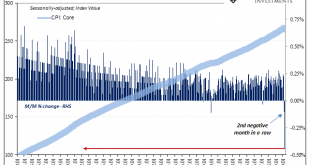
From a monetary policy perspective, smooth is what you are aiming for. What central bankers want in this age of expectations management is for a little bit of steady inflation. Why not zero? Because, they decided, policymakers need some margin of error. Since there is no money in monetary policy, it takes time for oblique “stimulus” signals to feed into the psychology of markets and the economy. Thus, a little steady inflation as insurance against the real evil....
Read More »We All Know Who’s On First, But What’s On Second?
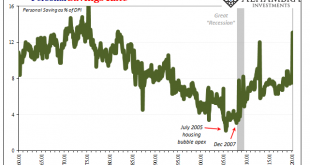
It wasn’t entirely unexpected, though when it was announced it was still quite a lot to take in. On September 1, 2005, the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) reported that the nation’s personal savings rate had turned negative during the month of July. The press release announcing the number, in trying to explain the result was reduced instead to a tautology, “The negative personal saving reflects personal outlays that exceed disposable personal income.” Why had it...
Read More » Swiss Economicblogs.org
Swiss Economicblogs.org