It’s that time again when the US government has to prepare itself for an internal battle to raise the debt ceiling so it can meet various obligations. This is a merry dance that has been danced before, as we mention below. For sure, every time it happens fewer and fewer people are convinced of the trustworthiness of the US dollar. This combined with the recent announcement by Saudi Arabia of its willingness to consider trading in currencies other than the US Dollar and the Euro suggests that the era of US Dollar hegemony may be in its final act. Every few years the U.S. government enters a debate over raising the National Debt Ceiling. This debate has dragged on for months in the recent past and will give the Fed a reprieve from being the center of the news for
Topics:
Stephen Flood considers the following as important: 6a.) GoldCore, 6a) Gold & Monetary Metals, Business, Commentary, Debt, Economics, economy, Featured, Geopolitics, News, newsletter, Politics, stock market
This could be interesting, too:
finews.ch writes Franken-Stablecoin-Vereinigung setzt Beirat ein
finews.ch writes Die stille Supermacht: Warum Indien für Investoren zunehmend relevant wird
finews.ch writes Spezielle Premiere an der Schweizer Börse
finews.ch writes Mehr Schweiz: AllianzGI macht den nächsten grossen Schritt
 It’s that time again when the US government has to prepare itself for an internal battle to raise the debt ceiling so it can meet various obligations. This is a merry dance that has been danced before, as we mention below.
It’s that time again when the US government has to prepare itself for an internal battle to raise the debt ceiling so it can meet various obligations. This is a merry dance that has been danced before, as we mention below.
For sure, every time it happens fewer and fewer people are convinced of the trustworthiness of the US dollar. This combined with the recent announcement by Saudi Arabia of its willingness to consider trading in currencies other than the US Dollar and the Euro suggests that the era of US Dollar hegemony may be in its final act.
Every few years the U.S. government enters a debate over raising the National Debt Ceiling. This debate has dragged on for months in the recent past and will give the Fed a reprieve from being the center of the news for the next few months.
The Debt Ceiling
The debt ceiling was created in 1917 under the Second Liberty Bond Act also known as the debt limit or statutory debt limit.
The debt ceiling is set by Congress and is the maximum amount that the U.S. Treasury Department can borrow by issuing bonds and when the ceiling is reached the U.S. Treasury Department must find alternative ways to pay expenses. The debt ceiling applies to most federal government debt (i.e. government bonds and Treasury bills).
It includes both debts held by the public and what the U.S. government owes as a result of “borrowing” from various accounts such as what it has “borrowed” from the Social Security and the Medicare trust funds.
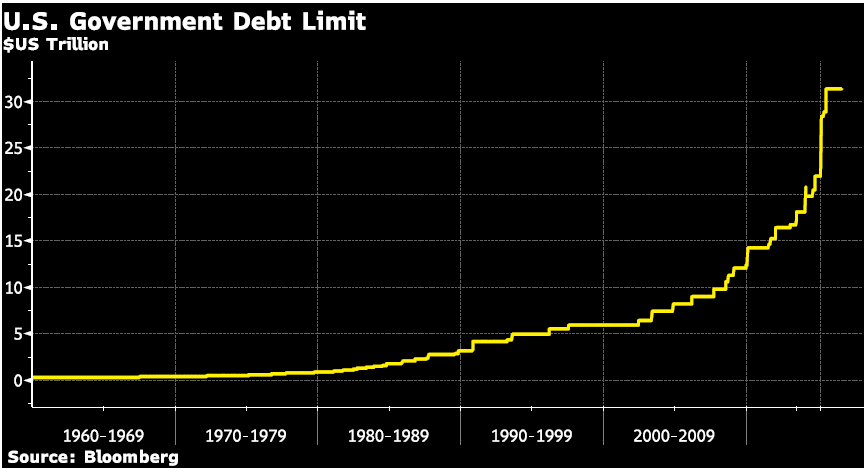
| The debt ceiling has been raised 78 times since 1960, the most recent time was in December 2021 to $31.4 trillion.
The debt ceiling went from just under $1 trillion to nearly $3 trillion in the 1980s and has roughly doubled every decade since – the 1990s saw it at $6 trillion, then by the end of the 2000s it stood at roughly $12 trillion, etc. When Congress raises the debt ceiling it has a good estimate of when the ceiling will be reached so it is not a surprise that it has been reached this month. U.S. Treasury secretary Yellen has told Congress that the debt ceiling will be reached on January 19 and it will have to resort to “extraordinary measures” (using cash reserves). Also, if the debt ceiling is not raised by early June the U.S. government will not be able to pay its bills as the extraordinary measures will be exhausted. |
|
US Government Debt LimitIn a formal letter sent to party leaders in Congress, Ms. Yellen said the government would hit the roughly $31.4 trillion borrowing limit on Jan. 19, when the Treasury Department will begin implementing so-called extraordinary measures to manage the government’s cash flow.
Congress raising the debt ceiling does not approve or incur any new spending, but instead, it authorizes the U.S. Treasury to borrow to pay for expenses that Congress has previously approved. With one exception the debt ceiling was raised as an ordinary course of business by Congress before 2010. The exception was in 1995 when a debate between the then Speaker of the House Newt Gingrich and then President Clinton clashed over spending cuts. With that, the government was shut down for 5 days (November 14-19, 1995) before an agreement was reached. However, with the increasingly divided Congress over the last dozen years, the process has become increasingly drawn out and very political between the Republicans and Democrats. This time is starting out the same with the House Republicans (who are now majority in the House) insisting that the raising of the debt ceiling comes with promises of spending cuts. And the Democrats (who control the White House and the Senate) are rejecting any type of spending cuts attached to raising the debt ceiling. |
What’s next?
In a worst-case scenario, Congress’s failure to raise the debt ceiling would put the U.S. government in default on its debts, and obligations and invoke a U.S. government shutdown.
The standoff between the Republicans and Democrats in 2011 over the debt ceiling increase resulted in declining equity markets and a downgrade of the U.S. credit rating. In August 2011 S&P downgraded the U.S. government debt from a 70-year-long triple-A rating to AA+.
In 2013 the US government was “shut down” for 16 days from October 1 to October 17 after “extraordinary measures” were exhausted after the debt ceiling was reached in January 2013.
Republicans in Congress used the debt ceiling as a political tool, to defund the Affordable Care Act (aka Obamacare). The standoff was resolved with the Continuing Appropriations Act, 2014 – which basically ‘kicked the debate down the road’.
Governments continue to add to their debt levels – and most likely pushing the debt ceiling debate to the limit of breaking Congress. Also, the White House will come to a resolution that will again ‘kick the can down the road’ as fiscal spending continues to rise.
However, a time will come when Congress pushes that little bit too far and faith in the U.S. dollar and debt is permanently damaged, and with so many countries already looking for alternatives to the U.S. dollar this will accelerate that momentum further.
And both individual investors and countries will turn to gold and silver as alternatives.
There are clearly plenty of alternatives to the US Dollar, but they are not all equal. We argue that gold and silver are by far the superior alternatives when it comes to insuring and protecting your portfolio against the mismanagement of both currencies and other investment classes. If you are interested to hear more about how to buy gold and silver, or why gold is being bought in record amounts then check out our YouTube channel.
Tags: Business,Commentary,debt,Economics,economy,Featured,Geopolitics,News,newsletter,Politics,stock market