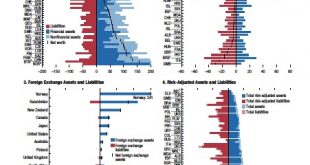
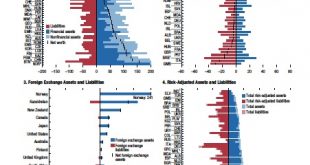
In its recent Fiscal Monitor, the IMF provides estimates of public sector net worth. See also this previous post.
Read More »Public Sector Net Worth
In its recent Fiscal Monitor, the IMF provides estimates of public sector net worth. See also this previous post.
Read More »“Reserves For All? Central Bank Digital Currency, Deposits, and their (Non)-Equivalence,” CEPR, 2018
CEPR Discussion Paper 13065, July 2018. PDF. (Personal copy.) I offer a macroeconomic perspective on the “Reserves for All” (RFA) proposal to let the general public use electronic central bank money. After distinguishing RFA from cryptocurrencies and relating the proposal to discussions about narrow banking and the abolition of cash I propose an equivalence result according to which a marginal substitution of outside for inside money does not affect macroeconomic outcomes. I identify key...
Read More »“Reserves For All? Central Bank Digital Currency, Deposits, and their (Non)-Equivalence,” CEPR, 2018
CEPR Discussion Paper 13065, July 2018. PDF. (Personal copy.) I offer a macroeconomic perspective on the “Reserves for All” (RFA) proposal to let the general public use electronic central bank money. After distinguishing RFA from cryptocurrencies and relating the proposal to discussions about narrow banking and the abolition of cash I propose an equivalence result according to which a marginal substitution of outside for inside money does not affect macroeconomic outcomes. I identify key...
Read More »“Financial Policy,” CEPR, 2018
CEPR Discussion Paper 12755, February 2018. PDF. (Personal copy.) This paper reviews theoretical results on financial policy. We use basic accounting identities to illustrate relations between gross assets and liabilities, net debt positions and the appropriation of (primary) budget surplus funds. We then discuss Ramsey policies, answering the question how a committed government may use financial instruments to pursue its objectives. Finally, we discuss additional roles for financial...
Read More »Government Debt with State Contingent Coupons
On VoxEU, Myrvin Anthony, Narcissa Balta, Tom Best, Sanaa Nadeem, and Eriko Togo discuss the history of government debt with state contingent coupons and offer some lessons. In the mid-19th century, the Confederate states issued cotton-linked bonds In the late 1970s, Mexico issued oil-linked bonds In the 2000s, Turkey issued revenue-indexed bonds Since 2014, Uruguay issues nominal wage-issued bonds Some other examples (figure taken from the column): Obviously, confidence in data quality...
Read More »Redistribution From Unexpected Deflation in the Euro Area
In the JEEA 14(4) (August 2016) Klaus Adam and Junyi Zhu argue that unexpected price-level movements generate sizable wealth redistribution in the Euro Area (EA) … The EA as a whole is a net loser of unexpected price-level decreases, with Italy, Greece, Portugal, and Spain losing most in per capita terms, and Belgium and Malta being net winners. Governments are net losers of deflation, while the household (HH) sector is a net winner … HHs in Belgium, Ireland, Malta, and Germany experience...
Read More »New Questions about Greece’s Indebtedness
On the FT’s Alphaville blog, Matthew Klein reports about discrepancies between IMF and Greek (and EU) assessments of Greek net indebtedness. The IMF appears to report lower Greek financial asset holdings than the Greek Central Bank. Matthew Klein quotes the Greek Central Bank: We would like to clarify that the Bank of Greece compiles its financial accounts, from which data on the general government’s net debt are derived, according to European standards. The Bank of Greece’s data are...
Read More »Heretical Thoughts and Doing the Unthinkable
Heresy! Legendary former hedge fund manager Stanley Druckenmiller at the Ira Sohn conference – not an optimist at present, to put it mildly. Photo credit: David A. Grogan / CNBC NORMANDY, France – The Dow rose 222 points on Tuesday – or just over 1%. But we agree with hedge-fund manager Stanley Druckenmiller: This is not a good time to be a U.S. stock market bull. Speaking at an investment conference in New York last week, George Soros’ former partner warned that… “…higher...
Read More »Weak CHF during the Fat Years of the Joseph Cycle
In December 2015, the seven year Joseph cycle ended with a Fed rate hike. These lean years of the Joseph cycle started in December 2008 when the Fed lowered rates to the current level. We think that in the next seven year cycle, even the risk-averse Swiss investors will buy more foreign assets, not only the central bank and speculators. Different crises have passed in the three parts of the world, the U.S. subprime, the euro crisis and the Emerging Markets crisis. The last one culminated...
Read More » Swiss Economicblogs.org
Swiss Economicblogs.org