On his blog, JP Koning offers two explanations for the surprisingly high rupee notes redemption rate—nearly 99%—after last year’s demonetization experiment: Money laundering, and a partial amnesty. Indians who had large quantities of illicit cash were able to contract with those who had room below their ceiling to convert illicit rupees on their behalf … Two weeks after the initial … announcement, the government introduced a formal amnesty for demonetized banknote holders. Any deposit of...
Read More »“Macroeconomics II,” Bern, Fall 2017
MA course at the University of Bern. Time: Wed 10-12. KSL course site. Course assistant: Christian Myohl. The course introduces Master students to modern macroeconomic theory. Building on the analysis of the consumption-saving trade off and on concepts from general equilibrium theory, the course covers workhorse general equilibrium models of modern macroeconomics, including the representative agent framework, the overlapping generations model, and possibly the Lucas tree model. Lectures...
Read More »“Sovereign Bond Prices, Haircuts, and Maturity,” IMF, 2017
CEPR Discussion Paper 12252, August 2017, with Tamon Asonuma and Romain Ranciere. PDF. (ungated IMF WP.) Rejecting a common assumption in the sovereign debt literature, we document that creditor losses (“haircuts”) during sovereign restructuring episodes are asymmetric across debt instruments. We code a comprehensive dataset on instrument-specific haircuts for 28 debt restructurings with private creditors in 1999–2015 and find that haircuts on shorter-term debt are larger than those on...
Read More »“Sovereign Bond Prices, Haircuts, and Maturity,” CEPR, 2017
CEPR Discussion Paper 12252, August 2017, with Tamon Asonuma and Romain Ranciere. PDF. (ungated IMF WP.) Rejecting a common assumption in the sovereign debt literature, we document that creditor losses (“haircuts”) during sovereign restructuring episodes are asymmetric across debt instruments. We code a comprehensive dataset on instrument-specific haircuts for 28 debt restructurings with private creditors in 1999–2015 and find that haircuts on shorter-term debt are larger than those on...
Read More »Babylonian Trigonometry, Ahead of Its Time By Thousands of Years
In Historia Mathematica, Daniel Mansfield and N.J. Wildberger argue that Plimpton 322, the Old Babylonian tablets, served as an exact ratio-based trigonometric table. … Instead, P322 is a trigonometric table of a completely unfamiliar kind and was ahead of its time by thousands of years. … we must adopt two ideas that are unique to the mathematical culture of the Old Babylonian (OB) period, between the 19th and 16th centuries B.C.E. First we abandon the notion of angle, and instead...
Read More »California
The Uerdingen Line Replaces The Wall
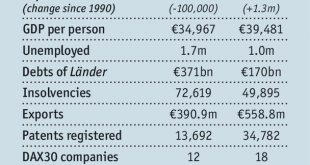
The Economist discusses the North-South divide in Germany which increasingly replaces the East-West division. The Southern states (Saarland, Rhineland-Palatinate, Hesse, Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria, Thuringia, Saxony) do better along many dimensions. Germans in the southern states … go to better schools, get jobs more easily, earn more and live longer to enjoy it. Their governments have healthier finances, so they can invest more … crime rates are “strikingly” lower in the south....
Read More »Long-Term Real Rates of Return
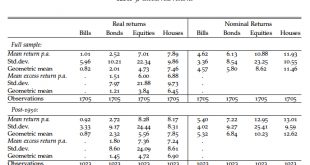
More from the recent working paper by Oscar Jorda, Katharina Knoll, Dmitry Kuvshinov, Moritz Schularick, and Alan Taylor (“The Rate of Return on Everything, 1870–2015“). (Previous blog post about the return on residential real estate.) Return data for 16 advanced economies over nearly 150 years … …on the income and capital gains (and thus, total returns) from equities, residential housing, government bonds, and government bills. Real returns average 7% p.a. for equity, 8% for housing,...
Read More »“Kunden sollten zwischen Sichtguthaben und elektronischem Notenbankgeld wählen können (Let People Choose Between Deposits and Reserves),” NZZ, 2017
NZZ, August 17, 2017. HTML, PDF. The Vollgeld initiative may point to a problem but it does not propose a viable solution. Even with Vollgeld, the time consistency friction with its Too-Big-To-Fail implication would persist. A more flexible, liberal approach appears more promising. It would give the general public a choice between holding deposits and reserves. Financial institutions and central banks around the world are pushing in that direction.
Read More »The Residential Real Estate Premium (Puzzle)
On Alphaville, Matthew Klein discusses recent work by Jorda, Knoll, Kuvshinov, Schularick, and Taylor (“The Rate of Return on Everything, 1870–2015“) according to which Residential real estate, not equity, has been the best long-run investment over the course of modern history. … but they didn’t calculate the returns most homeowners actually experience. Most people borrow to buy housing and most people live in their properties without renting them out. This makes a big difference. … Net...
Read More » Dirk Niepelt
Dirk Niepelt