Die Volkswirtschaft, 24 July 2020. PDF. Clarifying the connections between outright monetary financing, QE, the distribution of seignorage profits, the relationship between fiscal and monetary policy, and central bank independence. Abstract: Wenn Parlamentarier höhere Gewinnausschüttungen der Nationalbank fordern, Kritiker im Euroraum mehr «Quantitative Easing» oder Helikoptergeld verlangen und andere Stimmen monetäre Staatsfinanzierung monieren, dann steht die Beziehung zwischen...
Read More »“Wenn die Notenbank den Staat finanziert (When the Central Bank Finances the State),” FAS, 2020
FAS, 31 May 2020. PDF. Monetary deficit financing is the norm—after all, central banks distribute their profits. Monetary financing occurs in the context of regular open market operations and QE and, hyper charged, with helicopter drops. The question is not whether monetary policy should finance the government, but why it does so, and to what extent. Fiscal and monetary policy are inherently connected; what constitutes monetary policy is defined by objectives....
Read More »“Wenn die Notenbank den Staat finanziert (When the Central Bank Finances the State),” FAS, 2020
FAS, 31 May 2020. PDF. Monetary deficit financing is the norm—after all, central banks distribute their profits. Monetary financing occurs in the context of regular open market operations and QE and, hyper charged, with helicopter drops. The question is not whether monetary policy should finance the government, but why it does so, and to what extent. Fiscal and monetary policy are inherently connected; what constitutes monetary policy is defined by objectives.
Read More »“Moderne monetäre Theorie: Ein makroökonomisches Perpetuum mobile (The Macroeconomic Perpetuum Mobile),” NZZ, 2019
NZZ, April 25, 2019. PDF. Modern monetary theory (MMT) is neither a theory, nor modern, nor exclusively monetary. I discuss fallacies related to MMT. Dynamic inefficiency requires permanent, not transitory, r<g. For now, policy makers should rely on common sense rather than MMT.
Read More »“Moderne monetäre Theorie: Ein makroökonomisches Perpetuum mobile (The Macroeconomic Perpetuum Mobile),” NZZ, 2019
NZZ, April 25, 2019. PDF. Modern monetary theory (MMT) is neither a theory, nor modern, nor exclusively monetary. I discuss fallacies related to MMT. Dynamic inefficiency requires permanent, not transitory, r<g. For now, policy makers should rely on common sense rather than MMT.
Read More »ECB Bond Purchases: Fiscal or Monetary Policy?
In an NBER working paper, Arvind Krishnamurthy, Stefan Nagel, and Annette Vissing-Jorgensen analyze which components of bond yields were affected by the European Central Bank’s government bond purchasing programs. Given the institutional restrictions on monetary policy in the Euro area, the ECB had to carefully argue why it intervened in the first place. (To many, the case was obvious; the ECB intervention amounted to quasi-fiscal policy. But an intervention with this objective would not...
Read More »Independent Fiscal Institutions
In the FT blog, Peter Doyle emphasizes the importance of independent fiscal watchdogs. They matter. That’s why less autocratic governments pursuing competent policies support them (and others don’t). It would be useful to have independent fiscal institutions and policy watchdogs on a supranational level.
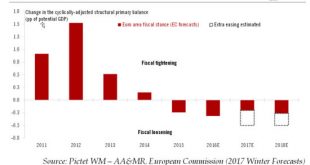
Read More »Euro area fiscal stimulus prospects
As the emphasis moves away from monetary initiatives, euro area GDP should benefit from a shift in fiscal policy going back to before the US elections.There has been growing evidence of a shift in the policy mix of various developed economies, from monetary to fiscal. In the euro area, we have likely entered a new cycle where the combination of austerity fatigue and greater flexibility on spending rules leads to more sustained fiscal support, however sub-optimal and uneven across countriesIn...
Read More »The Central Banks Pull Back: Now It’s Up to Fiscal Policy to “Save the World”
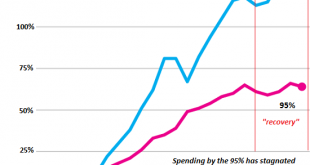
Another problem is the rise of social discord, for reasons that extend beyond the reach of tax reductions and increased infrastructure spending. Have you noticed that the breathless anticipation of the next central bank “save” has diminished? Remember when the financial media was in a tizzy of excitement, speculating on what new central bank expansion would send the global markets higher in paroxysms of risk-on joy?...
Read More »“Fehldiagnose Secular Stagnation (Secular Stagnation Skepticism),” FuW, 2016
Finanz und Wirtschaft, November 23, 2016. PDF. The diagnosis is far from clear. Nor is the therapy.
Read More » Swiss Economicblogs.org
Swiss Economicblogs.org