I will begin my remarks with a review of developments on the financial markets over the past half-year. I would then like to discuss the lowering of the threshold factor mentioned by Thomas Jordan. Situation on the financial markets Volatility on the financial markets has increased again significantly since the beginning of the year (cf. chart 1). This was driven by the sharp rise in inflation abroad and by attendant expectations regarding a speedier tightening of monetary policy – especially in the US. Indeed, the Fed has already raised the target range for its federal funds rate in several increments and signalled its intention to increase rates further. In addition, the war in Ukraine and the associated sanctions have exacerbated existing supply bottlenecks
Topics:
Andréa Maechler considers the following as important: 1.) SNB Press Releases, 1) SNB and CHF, Featured, newsletter
This could be interesting, too:
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Die Performance der Kryptowährungen in KW 9: Das hat sich bei Bitcoin, Ether & Co. getan
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Wer verbirgt sich hinter der Ethereum-Technologie?
Martin Hartmann writes Eine Analyse nach den Lehren von Milton Friedman
Marc Chandler writes March 2025 Monthly
I will begin my remarks with a review of developments on the financial markets over the past half-year. I would then like to discuss the lowering of the threshold factor mentioned by Thomas Jordan.
Situation on the financial markets
Volatility on the financial markets has increased again significantly since the beginning of the year (cf. chart 1). This was driven by the sharp rise in inflation abroad and by attendant expectations regarding a speedier tightening of monetary policy – especially in the US. Indeed, the Fed has already raised the target range for its federal funds rate in several increments and signalled its intention to increase rates further. In addition, the war in Ukraine and the associated sanctions have exacerbated existing supply bottlenecks and led to surges in energy and commodity prices. These developments have dampened growth expectations and increased uncertainty on the financial markets. |
Global Equity Markets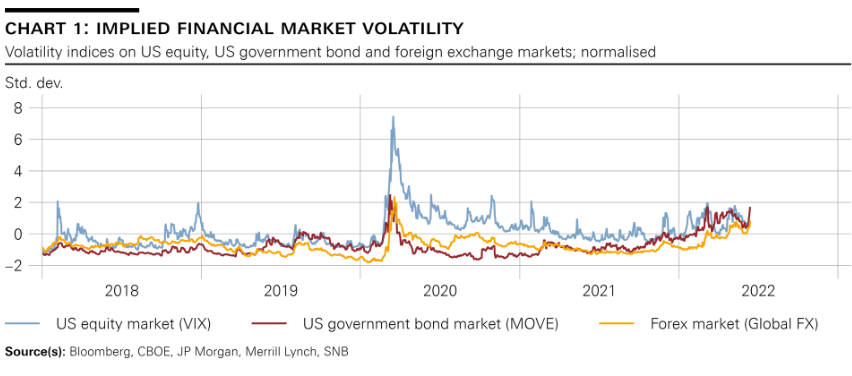 Source: www.snb.ch - Click to enlarge |
| On the government bond markets, the change in monetary policy direction has had a pronounced impact. In the US, nominal ten-year Treasury yields have risen almost 2 percentage points since the beginning of the year and most recently were standing at well above 3%. Shorter maturities were particularly affected by this revaluation, with a narrowing of yield differentials between long and short maturities. Such a flattening of yield curves is typical in a period of rising inflation and interest rate expectations. In the euro area, the corresponding yields on German government bonds also rose by almost 2 percentage points to about 1.7%. The rise in yields was similar in Switzerland, with ten-year Confederation bonds yielding around 1.3%, their highest level in more than ten years (cf. chart 2). |
10-Year Government Bond Yields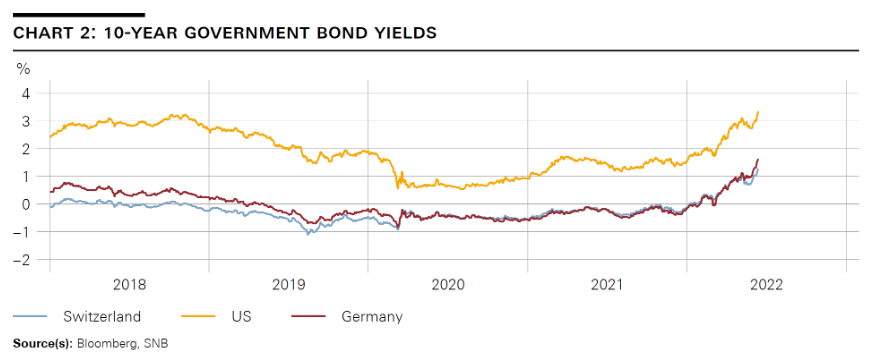 Source: www.snb.ch - Click to enlarge |
| In the US, the monetary policy realignment led to a considerable increase in inflation-adjusted bond yields, or real yields. For instance, real yields on ten-year Treasuries have risen by more than 1.5 percentage points since the beginning of the year and are now back at just above 0% for the first time in more than two years. In historical terms, however, this is still very low.
On the stock markets, too, the expectations of a tightening of monetary policy and the heightened uncertainty resulted in price corrections. The leading share indices have recently been trading at well below their levels at the beginning of the year, and the SMI, Switzerland’s leading index, has lost more than 15% over the same period (cf. chart 3). |
Implied Financial Market Volatility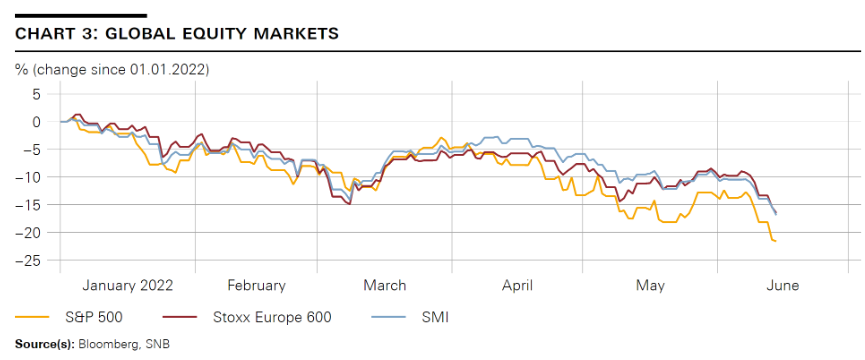 Source: www.snb.ch - Click to enlarge |
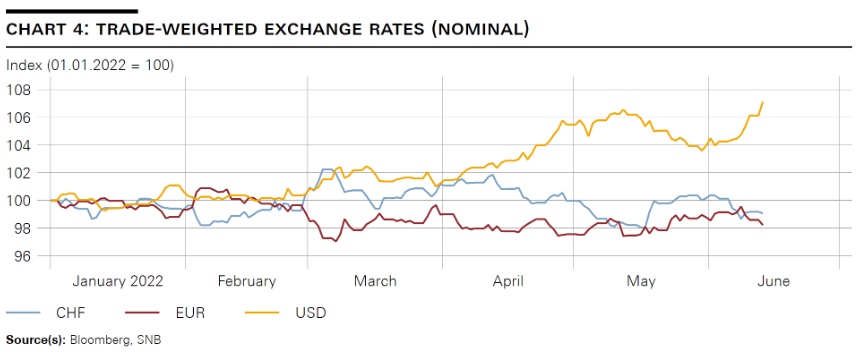
| Foreign exchange markets were likewise heavily shaped by the shift in monetary policy: The US dollar, for instance, has appreciated more than 7% on a trade-weighted basis since the beginning of the year. The trade-weighted euro, on the other hand, has lost around 1.5% and the Japanese yen has actually depreciated by more than 10% on a trade-weighted basis over the same period. The Swiss franc temporarily appreciated immediately following the outbreak of the war in Ukraine. The trade-weighted Swiss franc exchange rate, however, was recently below its level at the beginning of the year (cf. chart 4). |
Trade-weighted Exchange Rates |
Adjustment of the threshold factor
I would now like to discuss the lowering of the threshold factor from 30 to 28 as mentioned earlier by Thomas Jordan. With this technical adjustment, which will take effect from 1 July 2022, we will ensure that sufficient amounts of sight deposits are subject to negative interest, and that the latter is being passed on to the money market as intended.
From March 2022, upward pressure built up on the short-term rates on the secured money market. This stemmed from the fact that the exemption thresholds had risen over time due to the dynamic calculation model, which meant that there were no longer sufficient amounts of sight deposits subject to negative interest. To keep the secured short-term money market rates close to the SNB policy rate, the SNB provided additional liquidity to the money market via repo transactions as a temporary measure.
However, given that the increase in exemption thresholds is structural in nature, it is appropriate that we lower the threshold factor. This will result in the secured short-term money market rates being close to the SNB policy rate again without the SNB having to regularly provide larger amounts of liquidity.
The SNB will continue to regularly review the basis for calculating the exemption threshold and adjust it as necessary.
Tags: Featured,newsletter