In the NZZ, Hansueli Schöchli summarizes recent evidence. Wer in der Schweiz im Jahr 2017 wie viel Einkommenssteuer bezahlte Anteil Steuerpflichtige (in Prozent) Anzahl Steuerpflichtige Minimales Reineinkommen in Fr. Durchschnittliche Steuerbelastung (in %) Anteil der Einkommenssteuer Bund/Kanton/Gemeinde (in %) 0,01 515 4 548 020 43,8 4,82 0,1 5 150 1 109 760 37,3 9,89 1 51 498 331 731 34,4 24,04 5 257 489 152 799 28,1 42,55 10 514 978 111 403 24,6 53,03 25 1 287 444 73 769...
Read More »“Dynamic Tax Externalities and the U.S. Fiscal Transformation,” JME, 2020
Journal of Monetary Economics, with Martin Gonzalez-Eiras. PDF. (Appendix: PDF.) We propose a theory of tax centralization in politico-economic equilibrium. Taxation has dynamic general equilibrium implications which are internalized at the federal, but not at the regional level. The political support for taxation therefore differs across levels of government. Complementarities on the spending side decouple the equilibrium composition of spending and taxation and create a role for...
Read More »“Dynamic Tax Externalities and the U.S. Fiscal Transformation,” JME
Accepted for publication in the Journal of Monetary Economics, with Martin Gonzalez-Eiras. PDF. (Appendix: PDF.) We propose a theory of tax centralization in politico-economic equilibrium. Taxation has dynamic general equilibrium implications which are internalized at the federal, but not at the regional level. The political support for taxation therefore differs across levels of government. Complementarities on the spending side decouple the equilibrium composition of spending and...
Read More »“Dynamic Tax Externalities and the U.S. Fiscal Transformation,” JME
Accepted for publication in the Journal of Monetary Economics, with Martin Gonzalez-Eiras. PDF. (Appendix: PDF.) We propose a theory of tax centralization in politico-economic equilibrium. Taxation has dynamic general equilibrium implications which are internalized at the federal, but not at the regional level. The political support for taxation therefore differs across levels of government. Complementarities on the spending side decouple the equilibrium composition of spending and...
Read More »US Top Income Shares Rose Less Dramatically
That’s what Gerald Auten and David Splinter argue in a paper from last year. … new estimates of top income shares using two consistent measures of income. Our measure of consistent market income includes full corporate profits and adjusts for changes from TRA86, including changes to the tax base and increased filing by dependent filers. In addition, we include employer paid payroll taxes and health insurance and adjust for falling marriage rates. The effect of these adjustments on...
Read More »“Causes of the Transformation of the US Fiscal System in the 1930s,” VoxEU, 2016
VoxEU, October 11, 2016, with Martin Gonzalez-Eiras. HTML. The US fiscal system underwent a radical transformation around the time of the Great Depression. Perceived cost differences of revenue collection across levels of government, due to general equilibrium effects, can partly explain the rise of tax centralization and intergovernmental grants. We develop a micro-founded general equilibrium model that blends politics and macroeconomics. (See the working paper.)
Read More »Taxing the Rich
In Taxing the Rich: A History of Fiscal Fairness in the United States and Europe, Kenneth Scheme and David Stasavage explore the intellectual and political debates surrounding the taxation of the wealthy while also providing the most detailed examination to date of when taxes have been levied against the rich and when they haven’t. Fairness in debates about taxing the rich has depended on different views of what it means to treat people as equals and whether taxing the rich advances or...
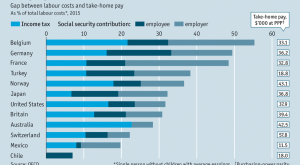
Read More »Tax Wedges
The average tax wedge in OECD countries has been stable over the last 15 years, at roughly 36 percent. OECD data. From The Economist, a decomposition in the cross section:
Read More » Swiss Economicblogs.org
Swiss Economicblogs.org