CEPR Discussion Paper 13065, July 2018. PDF. (Personal copy.) I offer a macroeconomic perspective on the “Reserves for All” (RFA) proposal to let the general public use electronic central bank money. After distinguishing RFA from cryptocurrencies and relating the proposal to discussions about narrow banking and the abolition of cash I propose an equivalence result according to which a marginal substitution of outside for inside money does not affect macroeconomic outcomes. I identify key...
Read More »A Taxonomy of Money
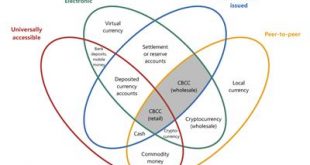
In a BIS Quarterly Review article, Morten Bech and Rodney Garratt offer a taxonomy of money, with special emphasis given to central bank issued digital and crypto currency. They stress four dimensions: issuer (central bank or other); form (electronic or physical); accessibility (universal or limited); and transfer mechanism (centralised or decentralised). The taxonomy defines a CBCC as an electronic form of central bank money that can be exchanged in a decentralised manner known as...
Read More »Should a Central Bank Issue Cryptocurrency?
On Alphaville, Izabella Kaminska asks why a central bank would want to issue cryptocurrency rather than conventional digital currency. … if anonymity is not the objective of issuing a centrally supervised cryptocurrency, what really is the point of using blockchain or crypto technology? Just issue a conventional digital currency and be done with it. If, on the other hand, anonymity is the objective of issuing a centrally supervised cryptocurrency, how can this be justified by a central...
Read More »Corporate Governance of Crypto Currencies
The Economist reports about conflicting strategies among important Bitcoin players; the struggle aligns pragmatists against libertarian ideologists. It also reports about attempts by competing crypto currencies to strengthen corporate governance: Tezos, another blockchain, will … not only have regular votes on competing proposals for how to change the system, but a more scientific approach to evaluating them and a way to compensate the developers for coming up with ideas. If their...
Read More »“Wer hat Angst vor Blockchain? (Who’s Afraid of the Blockchain?),” NZZ, 2016
NZZ, November 29, 2016. HTML, PDF. Central banks are increasingly interested in employing blockchain technologies, and they should be. The blockchain threatens the intermediation business. Central banks encounter the blockchain in the form of new krypto currencies, and as the technology underlying new clearing and settlement systems. Krypto currencies bear the risk of “dollarization,” but in the major currency areas this risk is still small. New clearing and settlement systems benefit...
Read More »Zcash
The Economist reports about a new digital currency platform, Zcash. The platform could handle more transactions than for example, Bitcoin. The open-source project backed by outside investors offers confidentiality: Bitcoin obscures the identity of currency owners, but the “blockchain”, the ledger that keeps track of all the coins, is open and can be analysed to see the flows of funds. This is a serious barrier for banks: blockchains could reveal their trading strategies and information...
Read More »“Central Banking and Bitcoin: Not yet a Threat,” VoxEU, 2016
VoxEU, October 19, 2016. HTML. Central banks are increasingly interested in employing blockchain technologies. The blockchain threatens the intermediation business. Central banks encounter the blockchain in the form of new krypto currencies, and as the technology underlying new clearing and settlement systems. Krypto currencies bear the risk of “dollarization,” but in the major currency areas this risk is still small. New clearing and settlement systems benefit from central bank...
Read More » Swiss Economicblogs.org
Swiss Economicblogs.org