We do not like Purchasing Power or Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) as measurement for currencies. For us, the trade balance decides if a currency is overvalued. Only the trade balance can express productivity gains, while the REER assumes constant productivity in comparison to trade partners. Who has read Michael Pettis, knows that a rising trade surplus may also be caused by a higher savings rate while the trade partners decided to spend more. This is partially true. Recently Europeans started to increase their savings rate, while Americans reduced it. This has led to a rising trade and current surplus for the Europeans. But also to a massive Swiss trade surplus with the United States, that lifted Switzerland on the U.S. currency manipulation watch list. To
Topics:
George Dorgan considers the following as important: 2.) Trade Balance News Service Bunt [FR], 2) Swiss and European Macro, Featured, newsletter
This could be interesting, too:
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Die Performance der Kryptowährungen in KW 9: Das hat sich bei Bitcoin, Ether & Co. getan
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Wer verbirgt sich hinter der Ethereum-Technologie?
Martin Hartmann writes Eine Analyse nach den Lehren von Milton Friedman
Marc Chandler writes March 2025 Monthly
We do not like Purchasing Power or Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) as measurement for currencies. For us, the trade balance decides if a currency is overvalued. Only the trade balance can express productivity gains, while the REER assumes constant productivity in comparison to trade partners.
Who has read Michael Pettis, knows that a rising trade surplus may also be caused by a higher savings rate while the trade partners decided to spend more. This is partially true.
Recently Europeans started to increase their savings rate, while Americans reduced it. This has led to a rising trade and current surplus for the Europeans.
But also to a massive Swiss trade surplus with the United States, that lifted Switzerland on the U.S. currency manipulation watch list.
To control the trade balance against this “savings effect”, economists may look at imports. When imports are rising at the same pace as GDP or consumption, then there is no such “savings effect”.
After the record trade surpluses, the Swiss economy may have turned around: consumption and imports are finally rising more than in 2015 and early 2016. In March the trade surplus got bigger again, still shy of the records in 2016.
Swiss National Bank wants to keep non-profitable sectors alive
Swiss exports are moving more and more toward higher value sectors: away from watches, jewelry and manufacturing towards chemicals and pharmaceuticals. With currency interventions, the SNB is trying to keep sectors alive, that would not survive without interventions.
At the same time, importers keep the currency gains of imported goods and return little to the consumer. This tendency is accentuated by the SNB, that makes the franc weaker.
Texts and Charts from the Swiss customs data release (translated from French).
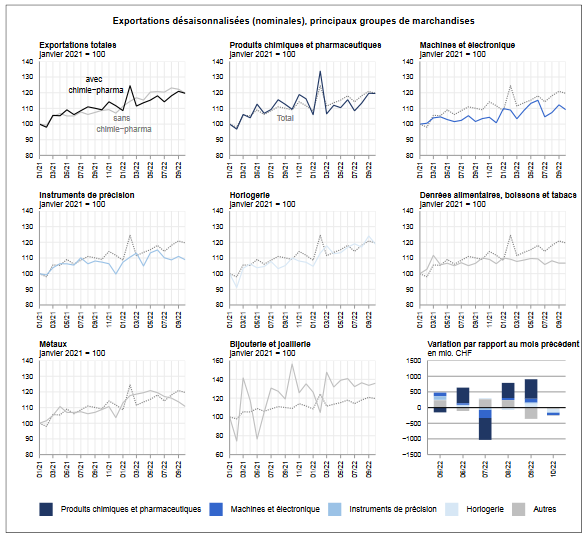
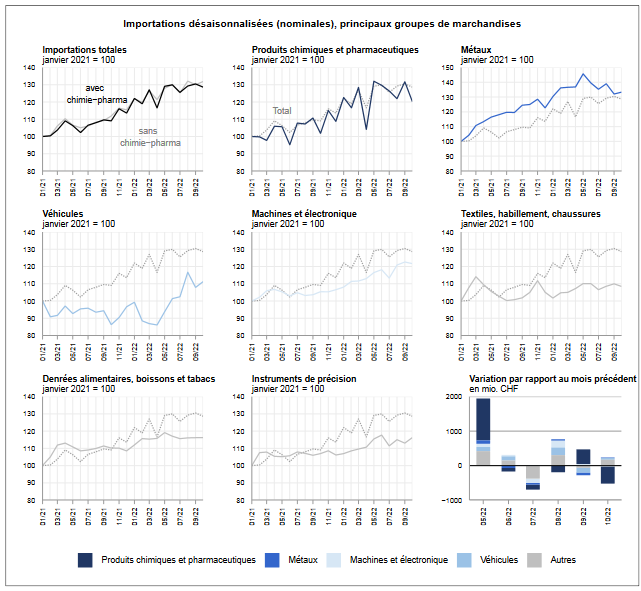
Exports and Imports YoY DevelopmentIn October 2022, Swiss foreign trade fell in both traffic directions. Exports contracted by 1.1% over one month and imports by 1.4%. On exit, the downturn affected a wide range of products, while on entry, the chemicals and pharmaceuticals sector dragged down results. The trade balance closes with a surplus of 3 billion francs. In short ⇓ Exports: Most Commodity Groups Decrease ⇓ Drug imports fall by 565 million francs ⇓ Contraction of trade with Spain and Slovenia (chemicals-pharma) ⇑ Shipments to the USA climb by 7.3% |
Swiss exports and imports, seasonally adjusted (in bn CHF), October 2022(see more posts on Switzerland Exports, Switzerland Imports, )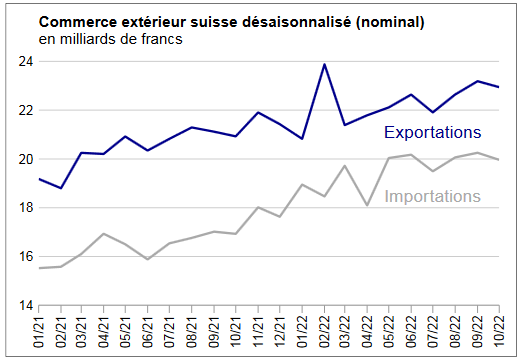 Source: newsd.admin.ch - Click to enlarge |
Global developmentIn October 2022 and after two consecutive monthly increases, seasonally adjusted exports fell by 1.1% (real: −1.8%). However, they remain on a positive trend. Imports fell by 1.4% over one month (actual: −0.8%), but have stagnated since the middle of the year. The trade balance ends with a surplus of 3 billion francs, the highest recorded in the last six months. |
Switzerland Trade Balance, October 2022(see more posts on Switzerland Trade Balance, )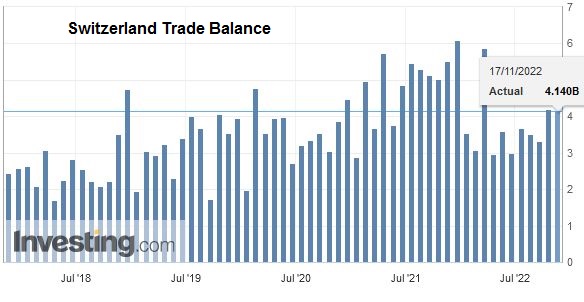 Source: investing.com - Click to enlarge |
|
Exports to China fall for the third month in a row
On exit, more than half of the commodity groups ended in the red in October 2022. Exports in the machinery and electronics sector fell by 78 million francs (−2.8%), after climbing the previous two months . Watches (−4.3%) and metals (−2.7%) also fell. The latter thus confirm their negative trend since their all-time high in May. Vehicles nevertheless suffered the heaviest setback (−125 million francs or −26%), after their takeoff the previous month. Chemicals and pharmaceuticals, for their part, stagnated. Here, gains in drugs offset losses in immunologicals and active ingredients.
From a geographical perspective, only exports to North America (+5.2%; USA: +7.3%) gained ground; those to the other two main markets fell back. Asia plunged 4.7% over one month while Europe lost 1.9%. On the Old Continent, Austria, Spain and Slovenia suffered the strongest contractions (cumulative: −593 million). The progression of Italy (energy products), which jumped by a quarter or 488 million francs, however made it possible to limit the breakage. On the Asian continent, the declines in China (−8.5%; third consecutive decline) and Japan (−8.9%) weighed on the result in particular.
|
Swiss Exports per Sector, October 2022 |
| The decline in chemicals and pharmaceuticals weighs on imports
On entry, the fall of half a billion francs in chemical and pharmaceutical products (−8.8%) tarnished the picture. Medicines suffered particularly, down by a fifth or 565 million francs; the previous month, however, these had increased by a third. Conversely, imports of vehicles – in particular aeronautics – increased by 3.1% (+52 million francs) while those of metals increased by 1.0% (+15 million). Arrivals of energy products stood out with an increase of 7.3% (+157 million); however, this was mainly due to the price effect (actual: +1.1%). A disparate trend characterized the three main supply markets: imports from North America and Europe fell by 3.7% and 1.2% respectively, while those from Asia increased by 3.3%, reaching a new high. On the European side, the fall of 290 million francs in Slovenia and Spain (chemicals-pharmaceuticals) pulled down the continental result. With the Asian partner, the rise of China and Japan (cumulative: +194 million francs) contrasted with the decline of Singapore (−143 million). |
Swiss Imports per Sector, October 2022 |
Tags: Featured,newsletter