Since the beginning of the year, the corona crisis has monopolized news coverage to the extent that a lot of very important stories and developments either went underreported or were ignored altogether. One such example was the very surprising ruling that came out of the German Constitutional Court in early May, which challenged the actions and remit of the European Central Bank (ECB). In essence, the court’s decision made it clear that the ECB’s quantitative easing (QE) program did not respect the “principle of proportionality,” abusing the ECB mandate, while the German government failed to challenge the bank’s policies as it should have. The ruling also mentioned the side effects of the program and of the ECB’s overall ultraloose policy direction, such as the
Topics:
Claudio Grass considers the following as important: 6b) Mises.org, Featured, newsletter
This could be interesting, too:
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Die Performance der Kryptowährungen in KW 9: Das hat sich bei Bitcoin, Ether & Co. getan
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Wer verbirgt sich hinter der Ethereum-Technologie?
Martin Hartmann writes Eine Analyse nach den Lehren von Milton Friedman
Marc Chandler writes March 2025 Monthly
Since the beginning of the year, the corona crisis has monopolized news coverage to the extent that a lot of very important stories and developments either went underreported or were ignored altogether. One such example was the very surprising ruling that came out of the German Constitutional Court in early May, which challenged the actions and remit of the European Central Bank (ECB).
In essence, the court’s decision made it clear that the ECB’s quantitative easing (QE) program did not respect the “principle of proportionality,” abusing the ECB mandate, while the German government failed to challenge the bank’s policies as it should have.
The ruling also mentioned the side effects of the program and of the ECB’s overall ultraloose policy direction, such as the penalizing of savers and pensioners. As was highlighted in the official decision, “the ECB fails to conduct the necessary balancing of the monetary policy objective against the economic policy effects arising from the program. Therefore, the decisions at issue…exceed the monetary policy mandate of the ECB.” As a result, the court issued an ultimatum and directly asked the Bundesbank to comply with its ruling and therefore to stop buying government bonds under the ECB’s QE program in the next three months.
Although the German court ruling had nothing to do with this latest wave of easing and money printing triggered by the coronavirus crisis, its timing puts the present situation in a different perspective.
This crisis has served as a “judgment day” of sorts. It has revealed the countless failures, the incompetence, and the disarray at the very core of most institutions, not just in Europe, but globally. The more decentralized nations fared relatively better than those with a high degree of centralization, the latter unfortunately being the majority. In the more centralized nations the lack of consistency and of clear leadership, the contradictory messages, the failures of public healthcare that cost countless lives, and the political decisions that cost millions their jobs and livelihoods all exposed the defects of centralization and the unreliability of both national governments and international organizations. And that’s just the first wave of disasters, the ones immediately seen and felt. There are even more grave consequences and aftereffects in the pipeline, which most citizens haven’t even realized yet, such as the inevitable breakdown of welfare systems and the debt time bombs in most major economies.
Specifically in the EU, the moral shortcomings, the small-time power games, the hypocrisy, and the sheer panic of the bloc’s leadership were laid bare for all to see. All that talk of friendship and cooperation between European nations, all the speeches about “solidarity” and the great European family, instantly proved shallow when this perfect union was confronted with the COVID threat. Shipments of medical supplies destined for one nation were seized in transit by its neighbor, drugs were hoarded, borders were shut down, trade was frozen. The first and hardest-hit member of the “family” went unaided and was helpless for weeks. The first EU rescue package, meant to help keep the economy alive in the face of the forced shutdown, was delayed by political horse trading, all while entire industries were decimated and millions rendered unemployed.
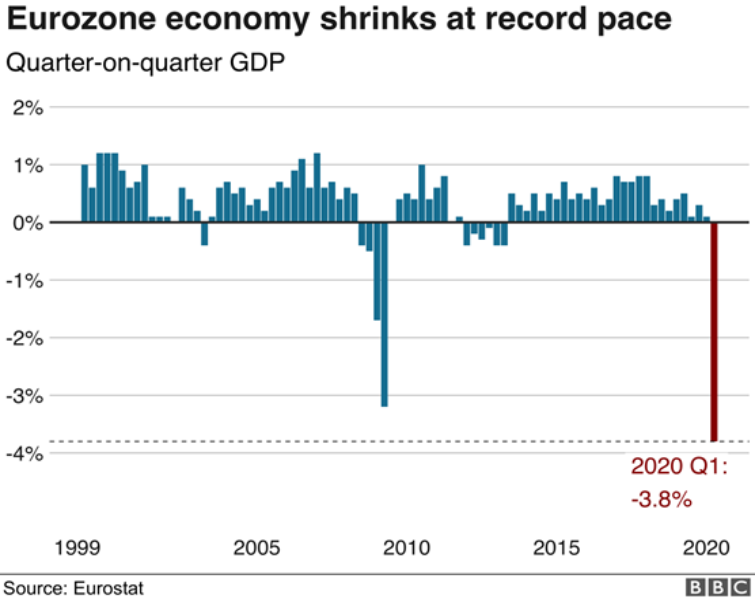
| The scale of the economic disaster is only now starting to become clear, and the future looks bleak even without all the risks being understood and accounted for yet. The deterioration and the economic downturn that is just beginning is projected to be comparable to or possibly worse than the Great Depression, and it could last longer too. Already the eurozone economy has seen the steepest decline in its history, according to Eurostat figures, while the unfolding recession is projected to be much worse than the last crisis. The “cures” that worked before are unlikely to stop this tsunami, while the unprecedented levels of spending we now see in most member states are not sustainable. The “emergency checks” and worker protections cannot stick around forever. Not unless they are formalized and normalized as we saw in Spain, where a basic income scheme is being introduced, the first ever in Europe, which the Spanish government hopes will indeed “stay forever.” This of course is no “solution,” but simply the nationalization of the economy. Central planning, income redistribution, and the state takeover of the private sector are all at the core of various “rescue” efforts and ideas being pushed at the moment, and we know where this road actually leads. If the countless historical examples aren’t enough to demonstrate the inevitable and inescapable results of these policies, one only need look at contemporary China. |
Eurozone Economy Shrinks at Record Pace, 1999-2020 |
Still, the economic pain is already so widespread that demonstrations and new movements are starting to have an impact. Antilockdown protests, rent strikes, and clashes with police have all been increasingly frequent in many European capitals. The political winds are also shifting, and once again public sentiment is turning decisively against the EU. According to a recent survey by Tecné, 42 percent of Italians said that they would leave the EU, up from 26 percent in November 2018, while 88 percent felt that the EU failed to support their country. Over in France, around six out of ten people “do no not trust” Brussels according to a Jacques Delors Institute study.
Therefore, this idea of nations taking back control of their economies couldn’t have come at a worse time for the EU and those who see an opportunity to push for further centralization in the corona crisis. Support for measures that would lead to tighter integration and even more power handed to Brussels is high among institutional figures; however, these plans are very unlikely to be popular among citizens.
Although the north-south economic divide has grown exponentially deeper in just a few months, the corona crisis has arguably managed to bridge political gaps. Citizens of the hard-hit south, especially in countries such as Italy and Spain, have become markedly more mistrustful and disillusioned with the EU and are turning away from it, as they feel that it turned away from them in their hour of need. On the other hand, citizens of the more prosperous north see exactly how this “rescue” effort is going to end, as it has a thousand times before, with them having to foot the bill to support southern economies that were already failing long before the coronavirus ever made it out of Wuhan.
What Lies Ahead
Overall, it is unlikely that the legal challenge from the German court will make a practical difference in the unlimited QE plans of the ECB. Especially at a time like this, negative interest rates and money flooding the markets are simply a fact of life, and there is no conceivable way for the ECB to just stop, the same way that it is impossible for governments to reverse course in their massive spending sprees anytime soon. The scale of the damage that has been done to the economy, the destruction of any kind of private productivity, the job-killing shutdowns, and the desperation among officials to plug the holes of a sinking ship all render these measures necessary, both politically and realistically.
What the court’s ruling might achieve, however, is not a monetary change, but a political one. It could serve as a signal that national sovereignty is still on the table, still worth debating and defending. In this regard, we do seem to be approaching a crossroads and there’s a choice to be made.
We either passively accept a centralized future, where the individual becomes irrelevant, valueless, and expendable, or we reclaim control, through the principles of subsidiarity, in which decisions are made on the lowest possible level and all voices are heard. In the aftermath of the corona crisis the latter option already seems to be gaining momentum, and understandably so. After so many were let down, betrayed, and ignored, after basic rights were trampled and the promise of security in exchange for freedom has proven to be a very bad deal indeed, it is no wonder that alternatives are sorely needed and that a hard turn toward individual responsibility, independent thought, and decentralization is already underway.
This article was originally published at claudiograss.ch.
Tags: Featured,newsletter