Swiss Franc The Swiss trade balance was published today, and once again, it remained close to record-high. For us, the trade balance is the most important indicator if a currency is fairly valued. Over the long-term the Swiss trade surplus must adjust towards zero, while the currency must appreciate. The consequence of the stronger currency is a higher purchasing power which leads to more spending and finally more imports. In recent years this has not happened yet, because the Swiss have increased their savings rate, while the Swiss National Bank prevented big parts of the necessary currency adjustment. Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com Monetary policy is said to have lost its impact on the foreign exchange market, as investors scratch their heads at the resilience of currencies with negative interest rates. Yet the price action in the action cannot be understood without recognizing the ongoing importance of monetary policy expectations. Two members of the UK MPC seemed to distance themselves from the dovishness of recent comments from Governor Carney and the minutes from the BOE meeting this week. They want more hard data post-Brexit.
Topics:
Marc Chandler considers the following as important: AUD, EUR, Featured, FX Daily, FX Trends, GBP, JPY, newsletter, U.K. Retail Sales, U.S. Existing Home Sales, U.S. Initial Jobless Claims, U.S. Philadelphia Fed Manufacturing Index, USD
This could be interesting, too:
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Die Performance der Kryptowährungen in KW 9: Das hat sich bei Bitcoin, Ether & Co. getan
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Wer verbirgt sich hinter der Ethereum-Technologie?
Martin Hartmann writes Eine Analyse nach den Lehren von Milton Friedman
Marc Chandler writes March 2025 Monthly
Swiss FrancThe Swiss trade balance was published today, and once again, it remained close to record-high. For us, the trade balance is the most important indicator if a currency is fairly valued. Over the long-term the Swiss trade surplus must adjust towards zero, while the currency must appreciate. The consequence of the stronger currency is a higher purchasing power which leads to more spending and finally more imports. In recent years this has not happened yet, because the Swiss have increased their savings rate, while the Swiss National Bank prevented big parts of the necessary currency adjustment. |
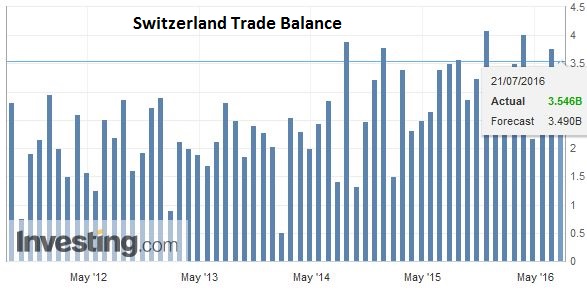 Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com |
Monetary policy is said to have lost its impact on the foreign exchange market, as investors scratch their heads at the resilience of currencies with negative interest rates. Yet the price action in the action cannot be understood without recognizing the ongoing importance of monetary policy expectations.
Two members of the UK MPC seemed to distance themselves from the dovishness of recent comments from Governor Carney and the minutes from the BOE meeting this week. They want more hard data post-Brexit. Sterling rallied a little more than two cents before the weaker than expected retail sales, whose survey period extended until July 2, saw it drop nearly three-quarters of a cent, leaving it little changed from yesterday’s NY close.
United KingdomFor the record, June UK retail sales fell 0.9%, which is half again as large of a decline as the median forecast (-0.6%). Food sales were off 1.2%, and non-food purchases fell 0.8%. The weaker consumer confidence surveys warn of downside risks going forward. We suspect that on balance the majority of the MPC will be inclined to ease policy next month, recognizing that monetary policy acts with a lag, even though the mark down of sterling may boost exports and spur some import substitution by domestic producers. |
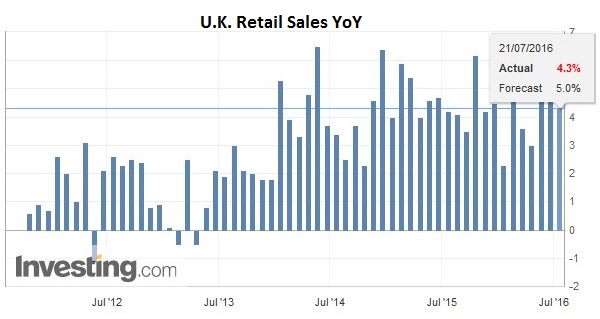 Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com |
JapanInitially, the focus in Japan was on fiscal policy. We had been highlighting the reports that suggested a large package (~JPY20 trillion) was under consideration, but in recent days, the media has been emphasizing a smaller package (~JPY10 trillion). However, today the talk is back at the larger figure, and this helped the dollar push through the JPY106.85 resistance we identified to reach almost JPY107.50. However, the dollar reversed lower, falling through yesterday’s lows seen near JPY105.85 (setting up a possible key reversal) in response to BOJ Governor Kuroda rejection of helicopter money. The market may have exaggerated the significance of Kuroda’s remarks, but it shows the nervousness of the market going into next week’s BOJ meeting after the dollar has rallied 7% against the yen since the US employment data on July 8. Our first target is near JPY104.65, and then possibly JPY103.75. First, it is not clear what Kuroda means by helicopter money. Some, like ourselves, have suggested that given the scale of the BOJ’s operations, and the fiscal position, Japan is already engaged in some form of helicopter money. An advisor to Abe agrees. Second, the idea of the MOF issuing a non-marketable perpetual bond that the BOJ would buy is not practical any time soon, though it has captured many imaginations. Like many other central banks, the BOJ is barred from buying bonds directly from the government. Third, in rejecting helicopter money, Kuroda kept the door open to extended QQE if needed. If the BOJ does not ease policy next week, the yen is likely to appreciate again. On the other hand, as investors have experienced, even if the BOJ does ease, it does not mean the yen will necessarily weaken. |
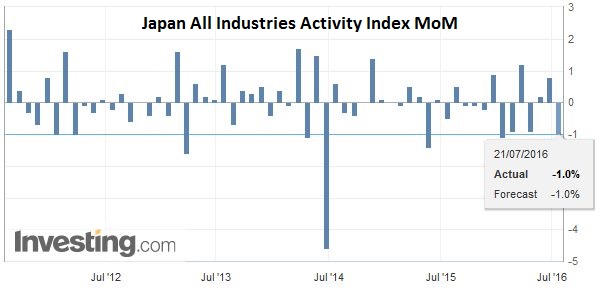 Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com |
European Central BankThe ECB meeting is one of the highlights of today’s sessions. The ECB’s focus has been on implementing the rest of its package of measures, like the corporate bond purchase program and the TLTRO. There are two issues that many investors may wish would be settled, but from the ECB’s point of view, there may be less urgency to decide now. First, will the ECB extend its QE past the current March 2017 soft end date? This can be decided after the summer when the staff forecast will be available, and more data will be in hand. It can be decided in Q4 as well.
|
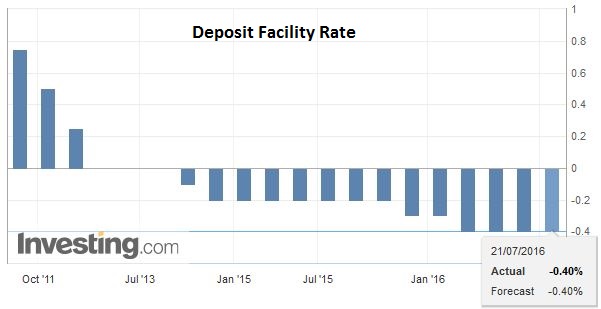 Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com |
| Second, with the further drop in interest rates since the UK referendum, more bund yields are below the deposit rate, which excludes them from the ECB purchase program. Many think the shortage is so acute that the ECB must decide something this week as September by being too late. We are less convinced that the ECB will feel their sense of urgency. And many observers seem too quick to suggest jettisoning the capital key criteria of the purchases. There are other measures that can be explored first that are less extreme. |
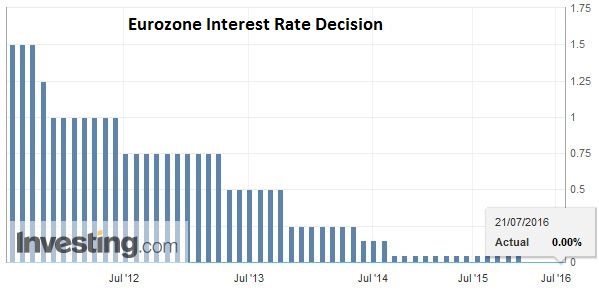 Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com |
FX RatesThe euro dipped below $1.10 yesterday for the first time since June 27. It has been confined a half-cent range above that floor today. Anticipate of Draghi either talking it down or being dovish may have weighed on it. There seems to be scope today then for sell the rumor buy the fact type of activity. The Reserve Bank of New Zealand was explicit. Further easing will likely be required. The New Zealand dollar is extending its recent losses. It has not posted an advancing sessions since July 12. It has lost about 5.2% against the US dollar in this period. It has found support as it approached the $0.6925-$0.6950 band that holds several technical levels. The Australian dollar is trading a little firmer having bounced off an important trendline near $0.7450. Expectations that next week’s Q2 CPI will not stand in the way of the RBA resuming its rate cuts has weighed on the Aussie. The market is discounting around a 60% chance of a cut next month. |
|
United StatesThe US reports weekly jobless claims, existing home sales and the July Philly Fed Business Outlook. Collectively the data does not have the heft to challenge the accumulated evidence that the US economy accelerated in late Q2, and that many regional Fed Presidents are more confident after being shaken by the poor May jobs report. |
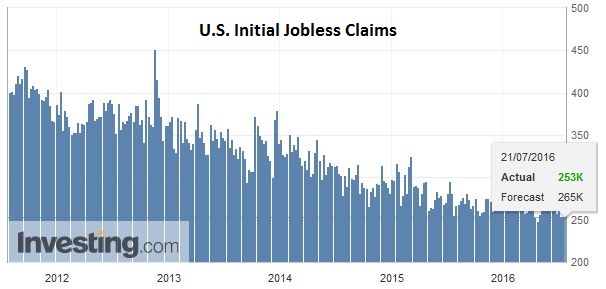 Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com |
U.S. Philadelphia Fed Manufacturing Index |
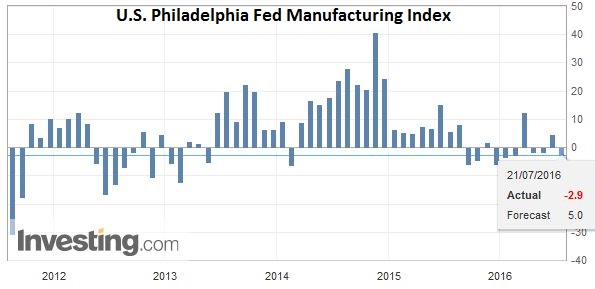 Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com |
U.S. Existing Home Sales |
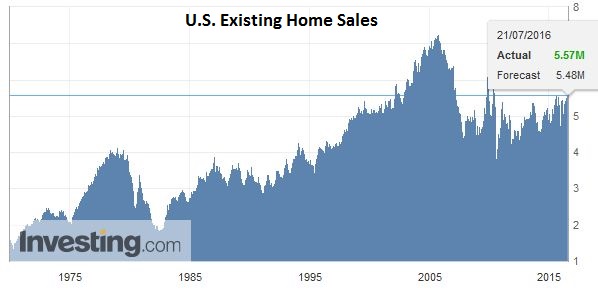 Click to enlarge. Source Investing.com |
Graphs and additional information on Swiss Franc by the snbchf team.