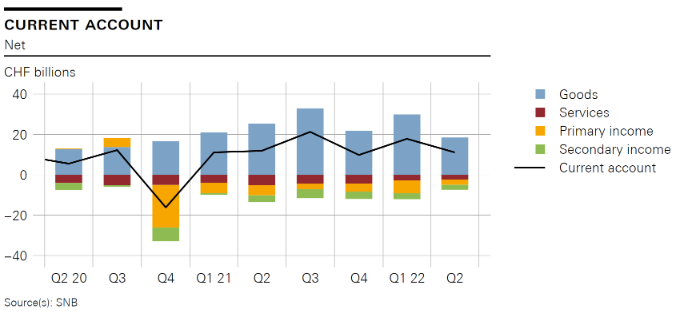
Overview In the second quarter of 2022, the current account surplus was CHF 11 billion, almost CHF 1 billion lower than in the same quarter of 2021. The receipts surplus in goods trade, especially merchanting and traditional goods trade (foreign trade total 1), declined. The expenses surpluses in services trade, primary income and secondary income were each lower than in the same quarter of 2021. . In the financial account, reported transactions recorded a net reduction of CHF 6 billion on the assets side and a net incurrence of CHF 7 billion on the liabilities side. The net reduction on the assets side was mostly attributable to ‘other investment’ because resident commercial banks decreased their claims on non-resident banks (interbank business). The net
Topics:
Swiss National Bank considers the following as important: 1.) SNB Press Releases, 1) SNB and CHF, Featured, newsletter, Switzerland Balance of Payments
This could be interesting, too:
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Die Performance der Kryptowährungen in KW 9: Das hat sich bei Bitcoin, Ether & Co. getan
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Wer verbirgt sich hinter der Ethereum-Technologie?
Martin Hartmann writes Eine Analyse nach den Lehren von Milton Friedman
Marc Chandler writes March 2025 Monthly
OverviewIn the second quarter of 2022, the current account surplus was CHF 11 billion, almost CHF 1 billion lower than in the same quarter of 2021. The receipts surplus in goods trade, especially merchanting and traditional goods trade (foreign trade total 1), declined. The expenses surpluses in services trade, primary income and secondary income were each lower than in the same quarter of 2021. |
|
| In the financial account, reported transactions recorded a net reduction of CHF 6 billion on the assets side and a net incurrence of CHF 7 billion on the liabilities side. The net reduction on the assets side was mostly attributable to ‘other investment’ because resident commercial banks decreased their claims on non-resident banks (interbank business). The net incurrence on the liabilities side was mostly attributable to direct investment, with resident companies receiving an inflow of funds from abroad in the form of intragroup lending. This was counteracted by resident commercial banks reducing their liabilities towards non-residents. Including derivatives, the financial account balance totalled CHF –12 billion.
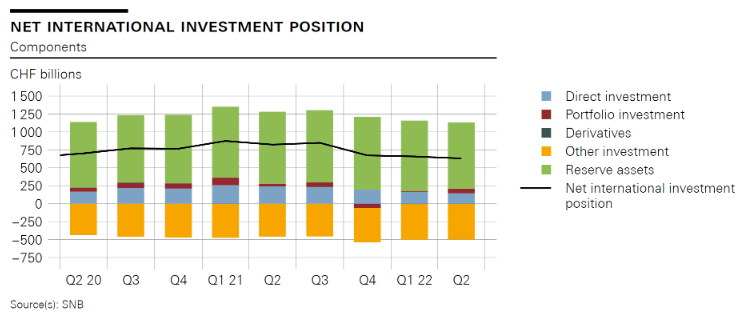
In the second quarter of 2022, the net international investment position declined by CHF 27 billion quarter-on-quarter to CHF 631 billion. Stocks of assets were down by CHF 156 billion to CHF 5,411 billion, and stocks of liabilities decreased by CHF 128 billion to CHF 4,780 billion. The decline in stocks on both the assets and the liabilities side was almost exclusively due to high price-related valuation losses, particularly in equities and bonds. |
Data revisions
The data on the current account take into account revisions, which extend over the entire period. These revisions were particularly significant between 2008 and 2021. On average, the current account balance decreased by around CHF 1.5 billion per quarter during this period.
These revisions were due to the closure of data gaps and newly available information from reporting institutions. More detailed information regarding these revisions is available under changes and revisions on the SNB’s data portal.
Further information
Comprehensive charts and tables covering Switzerland’s balance of payments and international investment position can be found on the SNB’s data portal. Detailed data are available in the supplementary data on international economic affairs datasets.
Tags: Featured,newsletter,Switzerland Balance of Payments