Summary:
“Experts” Assert that Inflation is an Agent of Economic Growth
For most experts, deflation, which they define as a general decline in prices of goods and services, is bad news since it generates expectations for a further decline in prices.
As a result, they hold, consumers postpone their buying of goods at present since they expect to buy these goods at lower prices in the future. This weakens the overall flow of spending and in turn weakens the economy.
Hence, such commentators hold that policies that counter deflation will also counter the slump. If deflation leads to an economic slump then policies that reverse deflation should be good for the economy.
Illustration via dailyreckoning.com – click to enlarge.
Reversing deflation would imply introducing policies that support general increases in the prices of goods, i.e., inflation. This means that inflation could actually be an agent of economic growth.
According to most experts, a little bit of inflation can actually be a good thing. Mainstream thinkers are of the view that inflation of 2% is not harmful to economic growth, but that inflation of 10% could be bad news (indeed the Fed’s inflation target is 2%).
Thus, we can conclude that at a rate of inflation of 10%, it is likely that consumers are going to form rising inflation expectations.
Topics:
Frank Shostak considers the following as important:
ceteris paribus,
Debt and the Fallacies of Paper Money,
Featured,
newsletter
This could be interesting, too:
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Die Performance der Kryptowährungen in KW 9: Das hat sich bei Bitcoin, Ether & Co. getan
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Wer verbirgt sich hinter der Ethereum-Technologie?
Martin Hartmann writes Eine Analyse nach den Lehren von Milton Friedman
Marc Chandler writes March 2025 Monthly
“Experts” Assert that Inflation is an Agent of Economic Growth
For most experts, deflation, which they define as a general decline in prices of goods and services, is bad news since it generates expectations for a further decline in prices.
As a result, they hold, consumers postpone their buying of goods at present since they expect to buy these goods at lower prices in the future. This weakens the overall flow of spending and in turn weakens the economy.
Hence, such commentators hold that policies that counter deflation will also counter the slump. If deflation leads to an economic slump then policies that reverse deflation should be good for the economy. |
 Illustration via dailyreckoning.com – click to enlarge. |
|
Reversing deflation would imply introducing policies that support general increases in the prices of goods, i.e., inflation. This means that inflation could actually be an agent of economic growth.
According to most experts, a little bit of inflation can actually be a good thing. Mainstream thinkers are of the view that inflation of 2% is not harmful to economic growth, but that inflation of 10% could be bad news (indeed the Fed’s inflation target is 2%).
Thus, we can conclude that at a rate of inflation of 10%, it is likely that consumers are going to form rising inflation expectations.
According to popular thinking, in response to a high rate of inflation, consumers will speed up their expenditure on goods at present, which should boost economic growth.
So why then is a rate of inflation of 10% or higher regarded by experts as a bad thing? Clearly there is a problem with the popular definitions of inflation and deflation. |
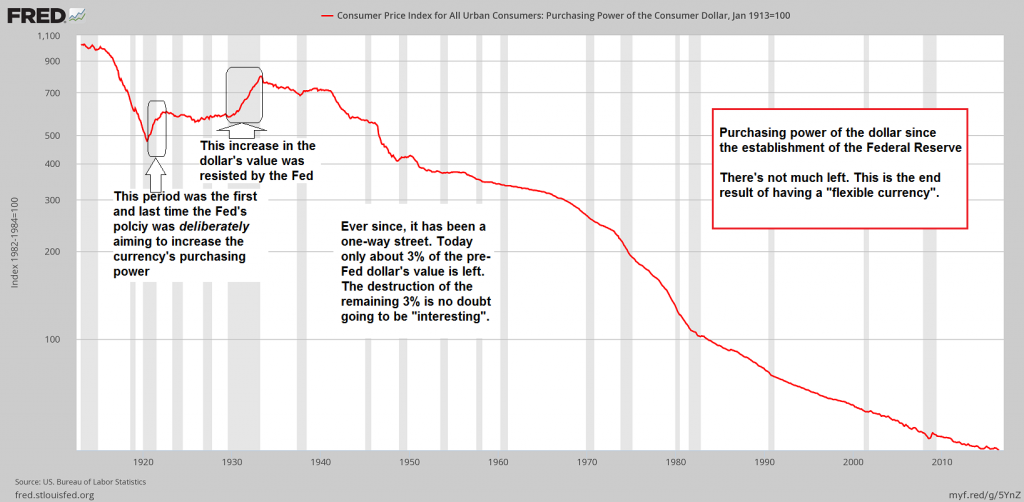 Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers. Purchasing Power of the Consumer Dollar, Jan 1913=100 – click to enlarge. This is a chart we have shown before. While acknowledging that it is simply not possible to measure the so-called “general level of prices” (no such thing exists), money certainly possesses purchasing power which is subject to constant change (this principle is valid regardless of what is used as money, even though some types of money, such as e.g. gold, are obviously more stable than others). Deflation as defined by the mainstream (i.e., “price deflation”) is the one thing that practically never happens under a fiat money standard. In fact, the Fed was only confronted with it twice in its history, even during the time when a bastardized version of the gold standard was still in place. It is fair to say that ever since the central bank has been established, the purchasing power of the dollar has been in near continuous collapse, with only the momentum of the decline occasionally changing. The fact that central bankers and a plethora of economists is actually worried about “deflation” is one of the most bizarre spectacles of modern times – in more than one respect . |
Inflation is Not Essentially a Rise in Prices
Inflation is not about general increases in prices as such, but about the increase in the money supply. As a rule the increase in money supply sets in motion general increases in prices. This, however, need not always be the case.
The price of a good is the amount of money asked per unit of it. For a constant amount of money and an expanding quantity of goods, prices will actually fall.
Prices will also fall when the rate of increase in the supply of goods exceeds the rate of increase in the money supply. For instance, if the money supply increases by 5% and the quantity of goods increases by 10%, prices will fall by 5%, ceteris paribus.
A fall in prices in this example cannot conceal the fact that we have an inflation of 5% here on account of the increase in the money supply. |
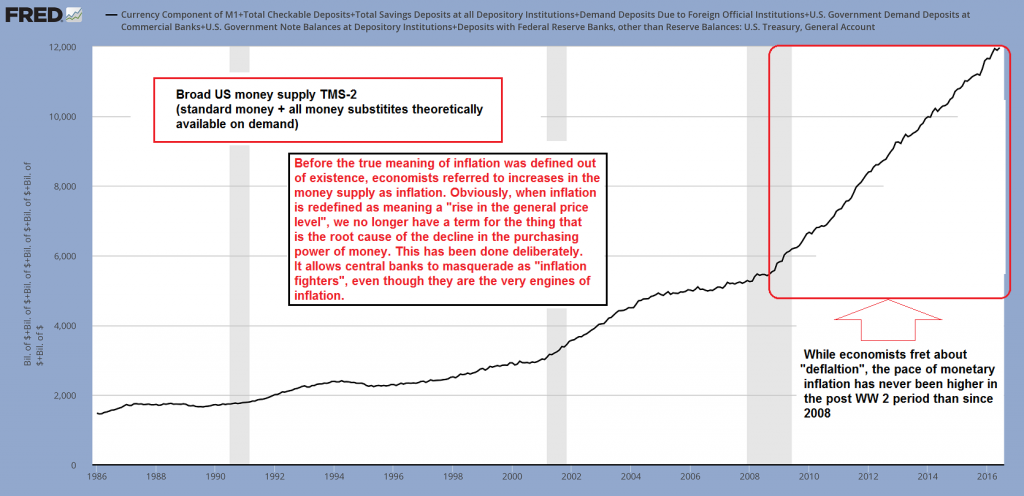 Broad US money supply TMS-2 – click to enlarge. An increase in the money supply is a necessary precondition for “price inflation” – but the ceteris paribus qualifier is very important, since prices are not only influenced by the supply of money, but also the demand for money, as well as the supply of and demand for goods and services. This is incidentally one of the reasons (in fact, the major one) why measuring the “general level of prices” is literally impossible: there exists no constant which can be employed in the measurement. |
Rising Prices Aren’t the Main Problem with Inflation
The reason why inflation is bad news is not because of increases in prices as such, but because of the damage inflation inflicts to the wealth-formation process. Here is why.
The chief role of money is to fulfill the role of the medium of exchange. Money enables us to exchange something we have for something we want.
Before an exchange can take place, an individual must have something useful that he can exchange for money. Once he secures the money, he can then exchange it for a good or goods he wants. Note that by means of money we have here an exchange of something for something.
But now consider a situation in which money is created out of “thin air” — this is precisely what the counterfeiter does. This type of money sets the platform for an exchange of nothing for something.
The counterfeiter exchanges the printed money for goods without producing anything useful. The counterfeiter takes from the pool of real goods without making any contribution to the pool.
The economic effect of money that was created out of thin air is exactly the same as that of counterfeit money — it impoverishes wealth generators. The money created out of thin air diverts real wealth toward the holders of new money. As a result, less real wealth is left to fund wealth-generating activities.
This in turn leads to a weakening in economic growth. Remember only wealth generating activities can generate wealth and hence grow an economy.
Note that as a result of the increase in the money supply what we have here is more money per unit of goods, and thus, higher prices. What matters, however, is not price rises as such but the increase in the money supply that sets in motion the exchange of nothing for something or “the counterfeit effect.”
The exchange of nothing for something, as we have seen, weakens the process of real wealth formation. Therefore, anything that promotes increases in the money supply can only make things much worse.
So while inflation is an increase in the money supply, deflation is a decrease in the money supply. We have seen that increases in the money supply, i.e., inflation gives rise to various non-productive activities, which we can also call “bubble activities.” |
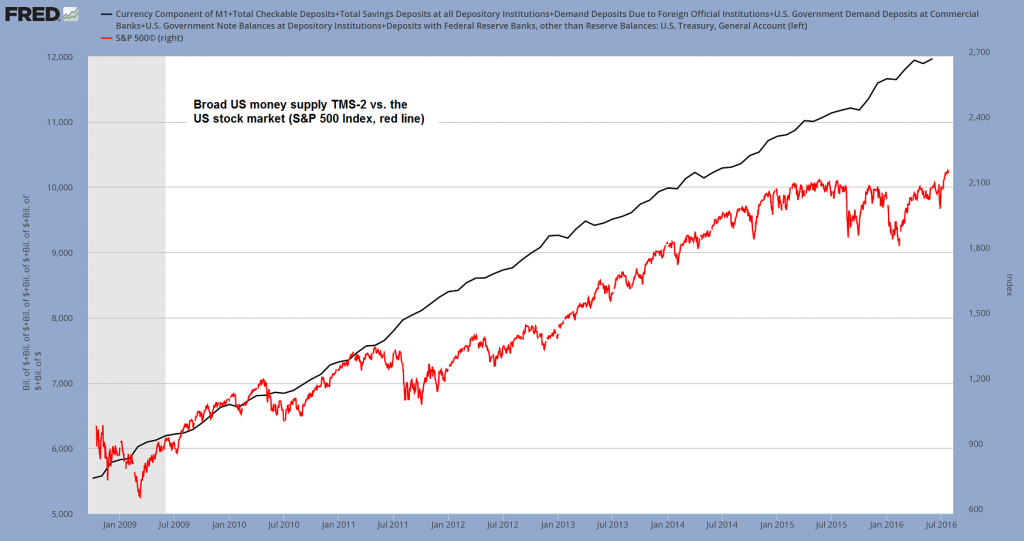 Broad US money supply TMS-2 vs. the US stock market (S&P 500 Index, red line) – click to enlarge. Money TMS-2 vs. the stock market (S&P 500 Index). Stocks are titles to capital, and as such tend to be particularly sensitive to monetary inflation. Note however that a rise in stock prices on account of monetary pumping is not a “sure thing” either. Still, we can certainly state that the huge and rapid surge in aggregate market capitalization in recent years is one of the symptoms of “bubble activities” caused by money supply expansion. |
Easy-Money Policies Divert Resources to Non-Productive Activities
Because these activities cannot stand on their own feet (they require the diversion of wealth from wealth generators) the increase in bubble activities on account of increases in the money supply weakens wealth generators’ ability to generate wealth.
Hence, loose monetary policies aimed at countering a fall in prices (i.e., fighting “deflation”), do nothing more than provide support for non-productive activities. Such policies can produce the illusion of success as long as there are enough wealth generators to fund non-productive activities.
For instance, in a company of 10 departments, 8 departments are making profits and the other 2 losses. A responsible CEO will shutdown or restructure the 2 departments that make losses.
Failing to do so will divert funding from wealth generators toward loss-making departments, thus weakening the foundation of the entire company. Without the removal, or restructuring, of the loss-making departments there is the risk that the entire company could eventually go belly up.
From this simple example we can deduce that once the percentage of wealth-generating activities falls sharply there will not be enough wealth to support an expansion in economic activity. The economy then falls into a prolonged slump. Under these conditions, the more the central bank tries to fix the symptoms, the worse things become.
Once, however, non-productive activities are allowed to go belly-up, and the sources of the increase in the money supply are sealed off, one can expect a genuine, real-wealth expansion to ensue. With the expansion of real wealth for a constant stock of money, we will have a fall in prices.
Conclusion
Note whether prices fall on account of the liquidation of non-productive activities or on account of real-wealth expansion, it is always good news. In the first case, it indicates that more funding is now available for wealth generation, while in the second case, it indicates that more wealth is actually being generated.
The major threat to the economy then is not deflation but policies aimed at countering it.
Charts by: St. Louis Federal Reserve Research
Chart and image captions by PT, emphasis in text added by PT
This article appeared originally at www.mises.org




