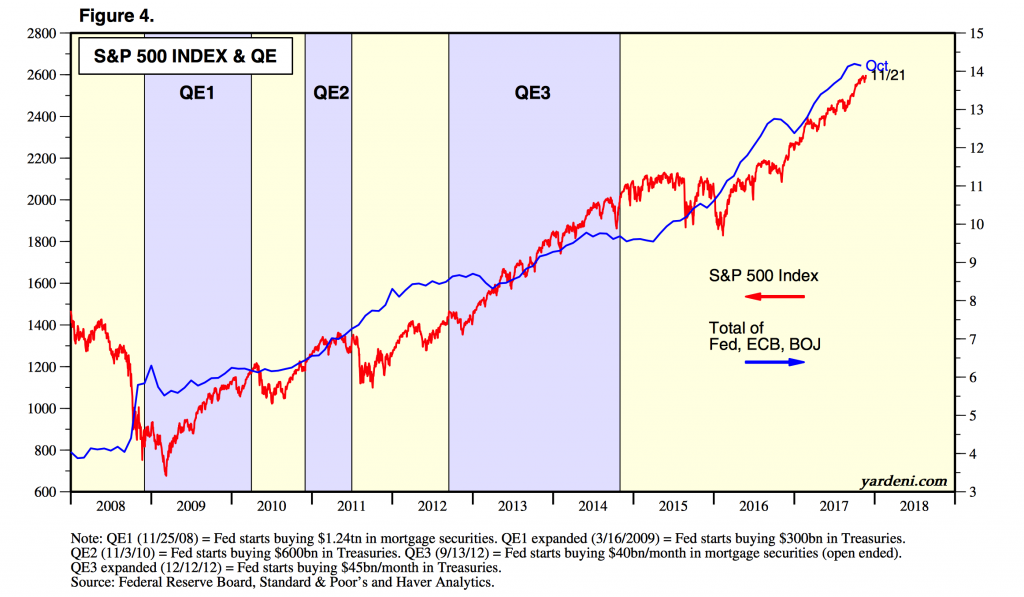
– FOMC minutes show uncertainty and concern about markets are affecting officials’ decision-making – Officials were cautious when evaluating market conditions and the ‘damaging effects on the economy’ – Worry about ‘potential buildup of financial imbalances’ and a sharp reversal in asset prices’ – Members seem oblivious to impact of inflation on households and savings – Physical gold and silver remain the only assets for real diversification and safety S&P 500 Index, 2008 - 2018(see more posts on S&P 500 Index, ) - Click to enlarge After nearly a decade of pumping up the US and global markets, Janet Yellen and team are now starting to show some concern for financial market prices. The FOMC is concerned that they
Topics:
Jan Skoyles considers the following as important: Featured, Financial Imbalances, GoldCore, newslettersent, S&P 500 Index, S&P 500 Index, Weekly Market Update
This could be interesting, too:
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Die Performance der Kryptowährungen in KW 9: Das hat sich bei Bitcoin, Ether & Co. getan
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Wer verbirgt sich hinter der Ethereum-Technologie?
Marc Chandler writes March 2025 Monthly
Mark Thornton writes Is Amazon a Union-Busting Leviathan?
| – FOMC minutes show uncertainty and concern about markets are affecting officials’ decision-making – Officials were cautious when evaluating market conditions and the ‘damaging effects on the economy’ – Worry about ‘potential buildup of financial imbalances’ and a sharp reversal in asset prices’ – Members seem oblivious to impact of inflation on households and savings – Physical gold and silver remain the only assets for real diversification and safety |
S&P 500 Index, 2008 - 2018(see more posts on S&P 500 Index, ) |
| After nearly a decade of pumping up the US and global markets, Janet Yellen and team are now starting to show some concern for financial market prices. The FOMC is concerned that they are getting out of hand and are a danger to the US economy.
The minutes of the Fed’s October meeting show that the committee is largely optimistic about the US economy:
But caution was the name of the game when it came to looking at overall market conditions:
There isn’t a huge amount you can say in response to the FOMC minutes. There was no surprise, they practically telegraphed a December rate hike. And, when it comes down to ‘financial imbalances’, you really just want to tweet them with ‘…no shi*t sherlock’. |
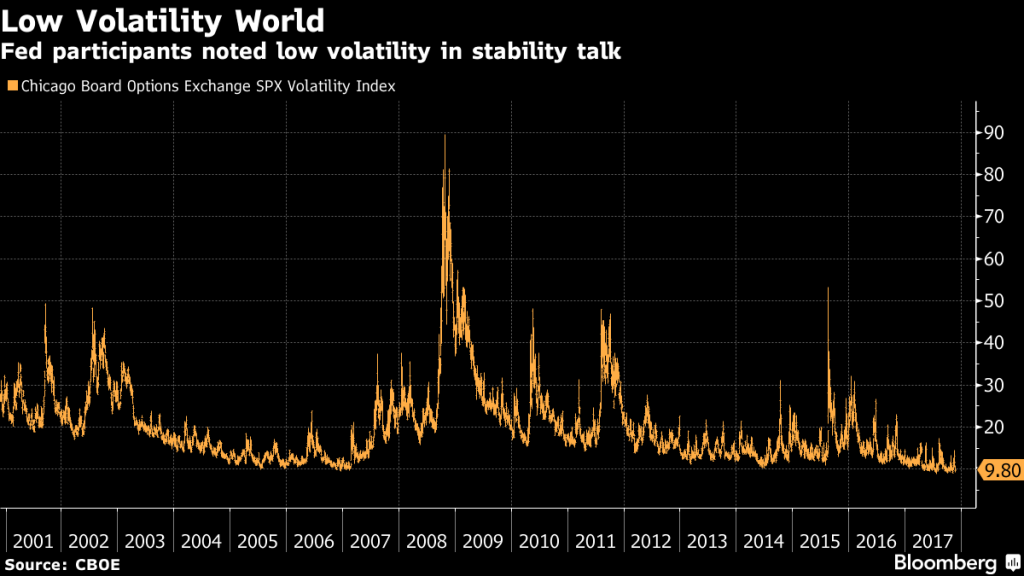
US Chicago Board Options, 2001 - 2017 |
| Why the sudden concern?
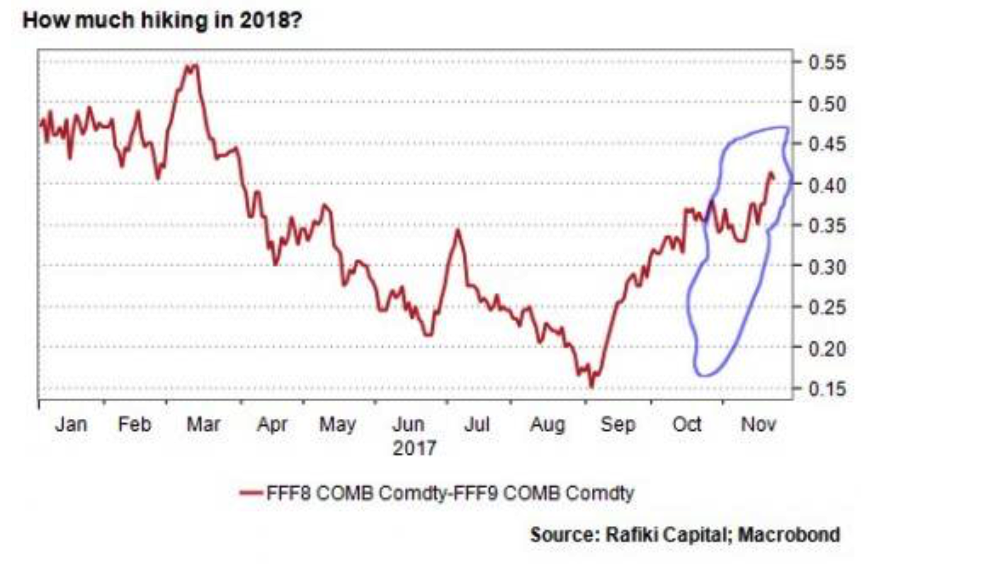
Really, why the sudden concern about financial imbalances? After all the FOMC has been pumping asset prices for the last decade. They are overjoyed to see the S&P500 regularly breaking through new highs. The ‘imbalance’ committee members refer to is likely in regard to the risk/reward profile in the price of equity markets. This is somewhat ironic given almost the exact same thing happened with bond markets thanks to QE and the Fed’s balance sheet expansion. Just consider that their own yield curve lies at the heart of the current equities bull market. The fear seems to be that in the last decade there has been such an expansion of credit that we are now faced with an unprecedented bubble. The Fed has no idea how this can be managed across central banks. They are concerned not only how the bubble will burs but what the contagion will be. Since the Fed started hiking rates up, markets and financial conditions have not tightened. At all. One could speculate that this shows the market is convinced that the moment equities suffer a selloff, the Fed will either stop hiking altogether, or (worse) revert to the status quo and announce QE4. At the moment the market is pricing in the risk of further rate hikes into next year. The chart below from HSBC shows “the market has been pricing in more and more 2018 hiking risk. The maroon line in the chart below shows the increase in hiking expectations in recent weeks, with investors pricing in more than 1 1/2 hikes for the first time since April.” |
Bloomberg Commodity Index, Jan - Nov 2017 |
| No matter market predictions of Fed rate rises no one can prepare for the aftermath of a $50 trillion debt build-up since the financial crisis of 2008. Nothing like this has been seen before.
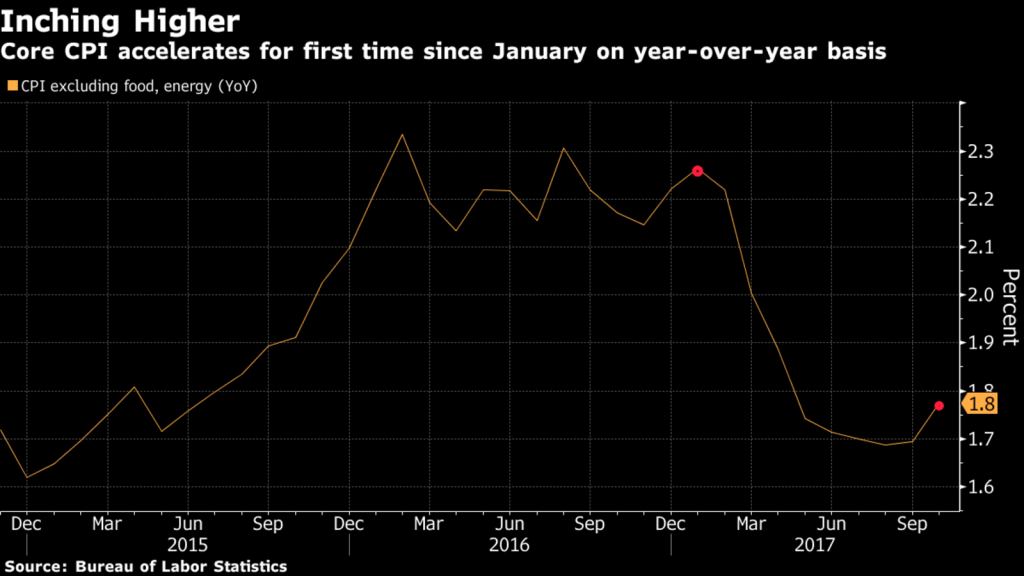
In this year alone we have hit a new record when it comes to money printing by central banks. Of course no one knows what we are dealing with. What is more concerning is that the world’s most powerful central bank is only now wondering about financial imbalances in the market. It’s a fix As has been the case in many Western countries, central banks have expressed frustration at the stubbornly low levels of inflation. What’s interesting about this is that many of them have spent a long time ensuring that the means by which inflation is calculated gets them closer to their target. The basket of goods used to calculate the level of price inflation is continuously manipulated.Very often ‘volatile’ food and fuel is not included in the US measure. Why does this matter? Because these are the two main items that affect household finances. So far this year US inflation has averaged 1.6% so far this year (when you exclude food and fuel) and it came in at just 1.3% in September. This (artificial) low level of inflation appears to have almost baffled FOMC members, with much disagreement amongst them. For those who believe inflation is low this “might reflect not only transitory factors, but also the influence of developments that could prove more persistent,” according to the minutes. However there were also a few members who expressed concern that it could begin to climb due to “increasing upside risks” to inflation as the labor market continues to tighten. It was then suggested by ‘a couple’ of members that the Fed tweak its approach to inflation, moving away from the current 2% target and toward a “gradually rising path” in prices instead. A nebulous approach. We continue to see a divided FOMC, with neither side getting our vote. As they continue to debate inflation and how to manage it, they are failing to do anything about it or even acknowledge what is really going on. It is concerning enough that the current inflation measures do not reflect the impact on households, savings and the depreciation of the US dollar. It is even worse when the FOMC is discussing whether they should even try and target inflation at all. Bill Blain of Mint Partners published an email from a reader expressing these very concerns with the FOMC:
|
US Core CPI, Dec 2015 - Sep 2017(see more posts on U.S. Core Consumer Price Index, ) |
| Not just a nervous Fed
The FOMC’s nervousness should be a cause for alarm but it should not be a feeling alien to market participants. They have long been concerned with the impact of central banks’ planned unwinding of balance sheets. A shift in monetary tightening has been identified in global surveys as the most likely cause of the next recession. These concerns are based in history. In 1994 the Fed began boosting rates, in a similar transition to today. The tightening triggered one of the worst corporate bond slides in two decades. The biggest loser was the suddenly devalued Mexican peso. Adding to this, three of the four most powerful central bank chiefs are set to be replaced. Expectations are that their successors will not want to be seen hanging around delaying monetary tightening. They will most likely continue to set aside inflation concerns in a drive to curb the financial excesses that they have encouraged for a decade. This will likely come with some problems, ones which the FOMC seems to be blind too. Yellen famously described balance sheet tightening as uneventful as ‘watching paint dry’. However, when one considers that more than half the gains in the S&P 500 from 2008 until the end of 2015 (when the FOMC began raising rates) came on days the Fed announced policy decisions then we should prepare for some harsh market reactions. A pantomime farce In the United Kingdom we have a very odd tradition at Christmas of ‘going to the pantomime’. The pantomime to those who haven’t been always seems to be a peculiar way to be entertained. It is not a pantomime as in a mime, as the word means in other countries, but instead it is a form of slap-stick musical entertainment. One of the ‘hilarious’ parts to every pantomime is when the hero is trying to catch the baddie of the show. The baddie keeps appearing behind the hero, but our protagonist always seems to not notice or just miss him. Meanwhile the audience’s calls for ‘He’s behind you!!’ grow louder and more raucous as the show goes on. The joke is, of course, that it seems to be near impossible that someone could miss a baddie looming so close and so obviously in the background. The same can be said of the FOMC and their apparent ignorance of the threat of ‘financial imbalances’ for the last decade. For years we have watched incredulously as the FOMC along with other central bank committees pump away at markets. It is as if we have come nearly to the end of the pantomime where the ‘hero’ is finally getting wise to the baddie’s tricks and is close to catching him. The only difference between a central bank pantomime and a real one is that there is unlikely to be a happy ending, as it will be the baddie who gets the better of the so-called ‘hero’. In this pantomime we do not know how it is supposed to end. How can we? Once again we conclude that this comes down to uncertainty. Whilst we have long-advocated for investors to line their portfolios with assets that offer true diversification and safety, it now seems more pertinent than ever. Central banks rarely admit that they are confused about the state of markets. This latest statement was the beginning of them starting to scratch their heads and admit they don’t have all the answers. As this uncertainty and confusion seeps through and grows, investors should be prepared for panic in both policy making and financial decisions. It is times like this when holding allocated, segregated gold in your portfolio makes even more sense. With a central bank wondering how to manage things, you can rest assured that your wealth is out of the reach of central bankers and their reactionary monetary policies. |
Betting on House |
Tags: Featured,Financial Imbalances,newslettersent,S&P 500 Index,Weekly Market Update