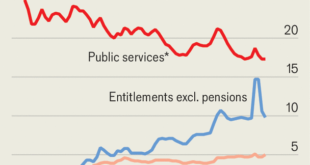
Says The Economist. The authors argue that falling state capacity, incompetence, corruption, and transfer/entitlement spending, which crowds out public investment and services, are to blame. Update: Related, in VoxEU, Martin Larch and Wouter van der Wielen argue that [g]overnments lamenting a stifling effect of fiscal rules on public investment are often those that have a poor compliance record and, as a result, high debt. They tend to deviate from rules not to increase public investment...
Read More »Public Sector Net Worth
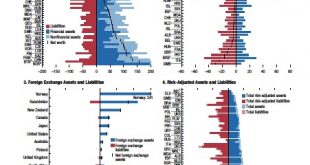
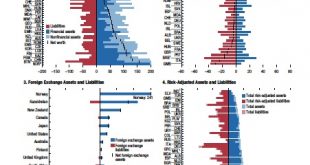
In its recent Fiscal Monitor, the IMF provides estimates of public sector net worth. See also this previous post.
Read More »Public Sector Net Worth
In its recent Fiscal Monitor, the IMF provides estimates of public sector net worth. See also this previous post.
Read More »Secular Stagnation Skepticism
I was asked to play devil’s advocate in a debate about “secular stagnation.” Here we go: Alvin Hansen, the “American Keynes” predicted the end of US growth in the late 1930s—just before the economy started to boom because of America’s entry into WWII. Soon, nobody talked about “secular stagnation” any more. 75 years later, Larry Summers has revived the argument. Many academics have reacted skeptically; at the 2015 ASSA meetings, Greg Mankiw predicted that nobody would talk about secular...
Read More » Swiss Economicblogs.org
Swiss Economicblogs.org