Onward vs. Upward Something both unwanted and unexpected has tormented western economies in the 21st century. Gross domestic product (GDP) has moderated onward while government debt has spiked upward. Orthodox economists continue to be flummoxed by what has transpired. What happened to the miracle? The Keynesian wet dream of an unfettered fiat debt money system has been realized, and debt has been duly expanded at every opportunity. Although the fat lady has so far only cleared her throat (if quite audibly, in 2008) and hasn’t really sung yet, it is already clear that calling this system careening toward a catastrophic failure. - Click to enlarge Here is the United States, since the turn of the new millennium (starting January 1, 2001) real GDP has increased from roughly .5 trillion to .6 trillion, or 77 percent. Over this same time government debt has spiked nearly 250 percent from about .7 trillion to .9 trillion. Obviously, some sort of reckoning’s in order to bring the books back into balance. Throughout this extended episode of economic and financial discontinuity, the government’s solution to jump-starting the economy has been to borrow money and spend it. Thus far, these efforts have succeeded in digging a massive hole that the economy will somehow have to climb out of.
Topics:
MN Gordon considers the following as important: Debt and the Fallacies of Paper Money, Featured, newsletter, On Economy, On Politics
This could be interesting, too:
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Die Performance der Kryptowährungen in KW 9: Das hat sich bei Bitcoin, Ether & Co. getan
Nachrichten Ticker - www.finanzen.ch writes Wer verbirgt sich hinter der Ethereum-Technologie?
Martin Hartmann writes Eine Analyse nach den Lehren von Milton Friedman
Marc Chandler writes March 2025 Monthly
Onward vs. UpwardSomething both unwanted and unexpected has tormented western economies in the 21st century. Gross domestic product (GDP) has moderated onward while government debt has spiked upward. Orthodox economists continue to be flummoxed by what has transpired. |
 What happened to the miracle? The Keynesian wet dream of an unfettered fiat debt money system has been realized, and debt has been duly expanded at every opportunity. Although the fat lady has so far only cleared her throat (if quite audibly, in 2008) and hasn’t really sung yet, it is already clear that calling this system careening toward a catastrophic failure. - Click to enlarge |
| Here is the United States, since the turn of the new millennium (starting January 1, 2001) real GDP has increased from roughly $10.5 trillion to $18.6 trillion, or 77 percent. Over this same time government debt has spiked nearly 250 percent from about $5.7 trillion to $19.9 trillion. Obviously, some sort of reckoning’s in order to bring the books back into balance.
Throughout this extended episode of economic and financial discontinuity, the government’s solution to jump-starting the economy has been to borrow money and spend it. Thus far, these efforts have succeeded in digging a massive hole that the economy will somehow have to climb out of. We’re doubtful such a feat will ever be attained. In short, additions of government debt over this time have been at a diminishing return. Specifically, at the start of the new millennium the debt to GDP ratio was about 54 percent. Today, it’s well over 100 percent. The idea that the government could spend borrowed money to grow the economy out of debt has become patently ridiculous. Nonetheless, government economists continue to advocate these policies because, academically, they have no other alternatives. At the same time, politics may now conspire to push the U.S. government into debt default. |
US GDP and Fedral Debt Indexed, 1984 - 2016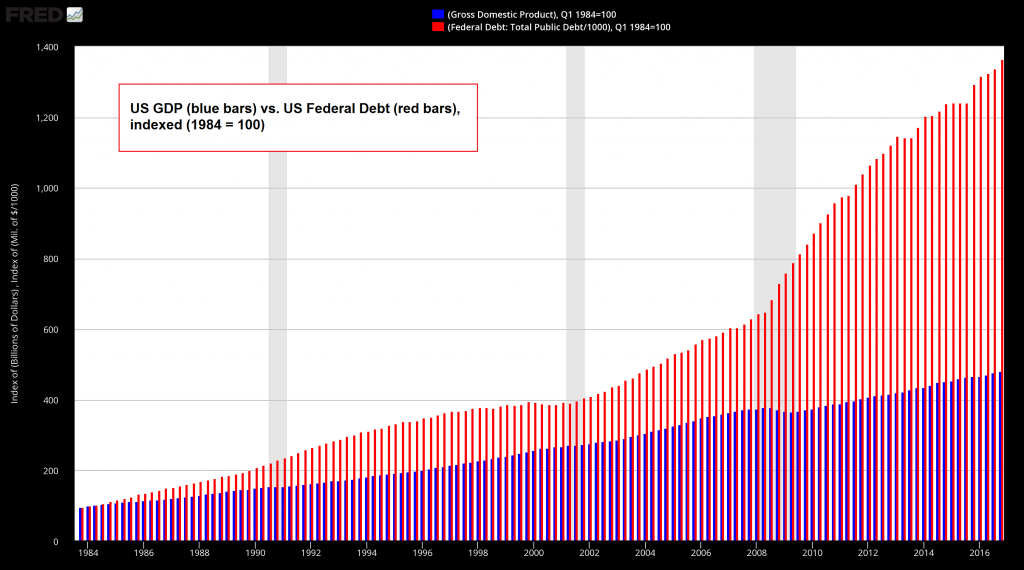 US GDP and US federal debt, indexed (1984 = 100). Mises noted back in the late 1940s already that “it is obvious that sooner or later all these debts will be liquidated in some way or other, but certainly not by payment of interest and principal according to the terms of the contract.” If it was obvious then, it is glaringly obvious today. Greece and Cyprus demonstrated what happens when modern socialist welfare states have no independent access to a printing press and are thus unable to extend and pretend in the traditional Keynesian way. The Potemkin village disintegrates on the spot at the first whiff of suspicion. All the nations that have postponed the reckoning by printing money and the flight forward mechanism of amassing even more debt have simply made the eventual denouement more profound - Click to enlarge |
Arrested DevelopmentThis week the Obama administration’s debt ceiling suspension expired, and a debt ceiling of $20.1 trillion was triggered. This reestablished debt ceiling is just a horse’s hair above the U.S. government’s current debt level. Furthermore, getting the debt ceiling lifted will likely require an epic Congressional battle, including elaborate displays of Kabuki theater. There’s a possibility a new debt ceiling agreement won’t be reached before the Treasury’s money runs out sometime in late-summer or early-fall. This would put the U.S. government in a position of not being able to pay its debts. At a minimum, even if some Congressional deal’s worked out at the 11th hour, the full faith and credit of the U.S. government will be tarnished. Best case, a timely debt ceiling resolution will cut into President Trump’s plans to boost the economy by borrowing money and spending it on infrastructure and defense. This will also cut into his plans to reduce taxes. A stumble in either of these areas could prompt a long overdue stock market panic. |
US Treasury Cash Balance. 2013 - 2017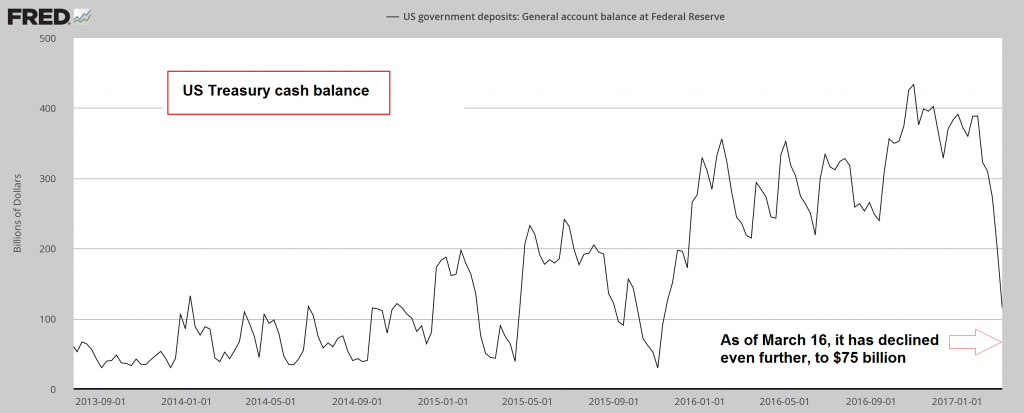 The debt ceiling could become a real problem this time, as the treasury has massively drawn down the cash balance it amassed by issuing humongous amounts of debt to US money market funds in 2016. In the final quarter of 2016, i.e., the dying days of the Obama administration, the federal deficit exploded by a stunning 208 billion dollars - Click to enlarge |
| The fact is, perpetual economic growth is required to sustain life as we know it in today’s debt-driven economic social order. Any slight blip, such as 2008, massively disrupts the lives of hundreds of millions of people. What’s more, economic growth must be at a level where the plebs believe they’re adequately reaping the fruits of their labors.
What that rate of economic growth happens to be is uncertain. But so far the U.S. economy of the 21st century has failed to attain it. What is known is that an economy that expands at 3 percent annually, will double the average living standard every 24 years. In contrast, an economy that expands at an annual rate of 2 percent, will take 36 years to double the average living standard. The average annual rate of real GDP growth of the U.S. economy in the 21st century has been at a 1.78 percent state of arrested development. The average annual rate of real GDP growth of the U.S. economy for the 16 preceding years was 3.43 percent – nearly double. Alas, it has been 12 years since the U.S. economy’s eked out a single year of 3 percent GDP growth. |
US GDP Annual Growth Rate, 1950 - 2015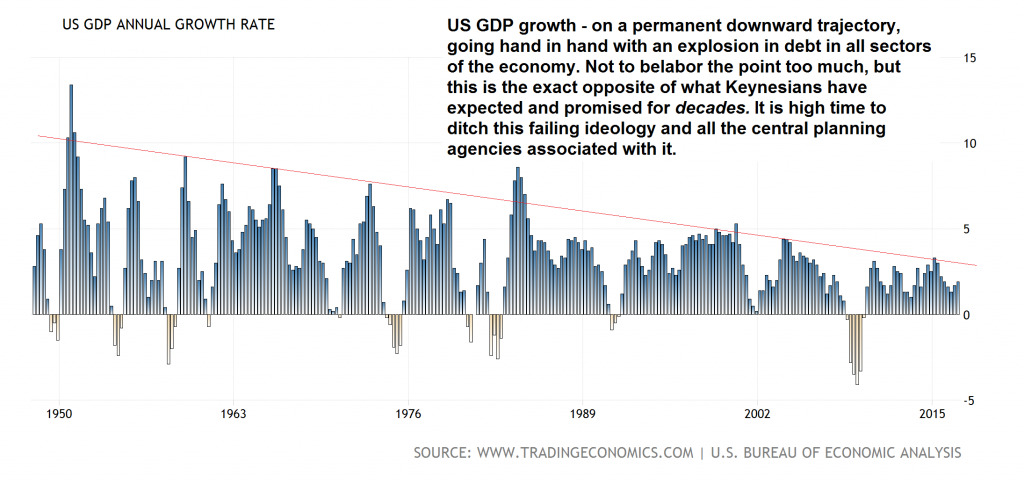 In spite of statistical distortions reaching fresh heights of absurdity year after year (their goal is generally to make “inflation” look smaller and GDP larger than they really are), economic output as measured by GDP is seemingly on a permanent downward trajectory. Many European countries look even worse. For instance, France had strong growth for more than two decades after WW2, but it collapsed thereafter. Today, government spending in France accounts for 58% of GDP and the country’s microscopic growth rates have become downright embarrassing. But don’t worry, Europe’s political elites and bureaucrats continue to prosper! - Click to enlarge |
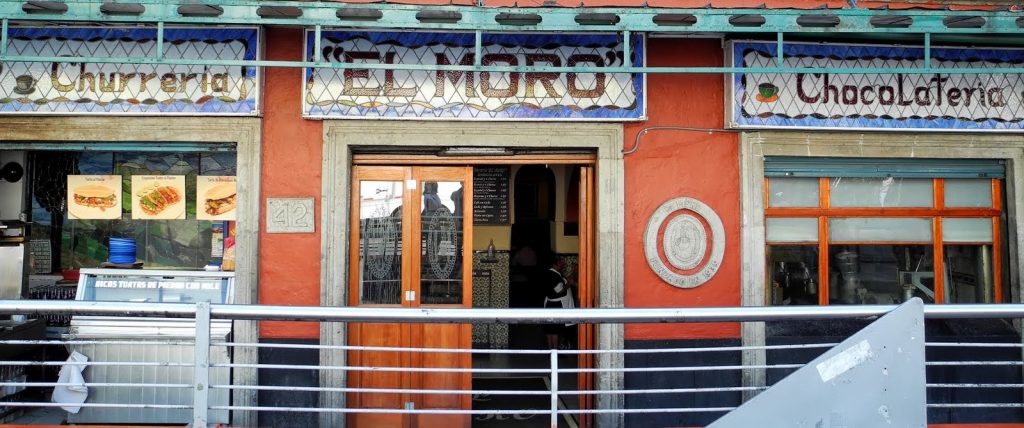
The Long Run Economics of Debt Based Stimulus“In the long run, we are all dead,” said 20th Century economist, John Maynard Keynes. This, in a nut shell, was Keynes’ rationale for why governments should borrow from the future to fund economic growth today. Why wait for recessions to do the work of equilibrating the economy when a little counter-cyclical stimulus can push growth onward and upward? Of course, attempting to spend a nation to prosperity using borrowed money is not without consequences. In the short run, an illusion of wealth can be erected. In the long run, that illusion slips into decay and disrepair. Over the past week we’ve been roaming the streets of Mexico City, visiting family and conducting field research on your behalf. In particular, we’ve been investigating the chronic effects of what happens when a government spends too much borrowed money, and then attempts to lighten its debt burden by inflating its currency. What follows a brief summation of our findings. On surface, what happens is what you’d expect. The currency gets utterly destroyed. This has the effect of blowing the price of just about everything – especially imports – through the roof. But it’s what happens after which is less obvious. For the ill-effects of a debased currency express themselves in asymmetric ways. |
 J.M. Keynes is certainly dead, but we are still alive and can rightly be referred to as his victims. Keynes is often depicted reading a book, but evidently he must have read the wrong book. And all those who assert that he “didn’t really mean it this way or that way” should perhaps take the time to read what he wrote. Keynes really was a Keynesian! Photo credit: Keystone/DPA - Click to enlarge |
| On a Saturday afternoon walk through the historic city center along Avenida Francisco I. Madero between El Zócalo and the Palacio de Bellas Artes we were greeted with the appearance of consumer prosperity. Bustling crowds of shoppers made their way through the chic fashion stores that are interspersed between historic 17th and 18th century colonial mansions and buildings. Modern skyscrapers were in the distance.
Similarly, during a Friday night visit to El Moro, the famous churro and chocolate restaurant that has been in operation since 1935, we encountered a line extending out the door and down the street. Customers were dressed to impress. There was hardly a hint of economic hardship about the place. But venture outside the most inner streets of the city’s center and the conditions quickly deteriorate. An endless sea of multilevel residential dwellings mixed with commercial and industrial properties in varying degrees of decay extend for miles and miles across the high altitude Valley of Mexico. It appears that, perhaps 50 or 60 years ago, these structures were clean and well-kept. However, that was before crumbled concrete and exposed rebar became the norm for these vast residential dwellings. Contrary to what Keynes posited, counter-cyclical debt based stimulus didn’t produce the nirvana of rising long run living standards. Rather it produced the disparity of stagnating GDP and rapidly rising government debt. Later it produced the hell of declining living standards over the long run. The truth is, in the long run we’re not all dead. Actually, some of us are still here, living with the consequences of shortsighted economic policies. |
|
| Residents of Mexico know this all too well. In the United States, the scope and magnitude of debt has been able to support an illusion of prosperity. Still, as far as we can tell, many residents are experiencing the transformation of small pockets of slums into vast expansive ghettos.
Storing up a small hoard of gold and silver bullion may’ve never been more critical than the present, in the off chance the inevitable dollar debasement comes sooner rather than later. So, too, one would be well advised to develop a side hustle now. From our observation, everyone in Mexico City was working… though many didn’t have jobs. On Monday we traveled north of the city limits to the ruins of the ancient pre-Aztec city of Teotihuacán. There we climbed up the Pyramid of the Sun and into the open areas of the Pyramid of the Feathered Serpent. We walked the Avenue of the Dead toward the Pyramid of the Moon. |
 Teotihuacán – view from the pyramid of the moon. Aztec priests once ripped out the hearts of sacrificial victims to appease their gods (among those in need of appeasing were Huiztilopochtli, the god of war and the sun, Tlaloc the rain god and not to forget, good old Xipe, a.k.a. “Our Lord, the Flayed One”, god of sacrificial pain and suffering. And you should see their mama… (wait for it). The Aztecs had a god for everything, so there was a lot of sacrificing to do. Photo via alcafocha - Click to enlarge |
| At its peak, around 450 AD, Teotihuacán was the largest city in the pre-Columbian Americas, with a population estimated at 150,000. Yet by the 6th century the population began to decline and the city ceased to exist sometime in the 7th or 8th century. No one quite knows what happened.
One theory is that the city’s decline coincided with an extended drought. Another is that there was an internal uprising. Maybe a 99 percent situation developed. We kicked a few rocks. We put our ears to the ground. We looked. We listened. The spirits didn’t answer. They didn’t have to. We’d already seen and heard enough. |
Charts by St. Louis Federal Reserve Research, TradingEconomics
Chart and image captions by PT
Tags: Featured,newsletter,On Economy,On Politics


